10 Best Practices for Mobile App Development in 2026

In the hyper-competitive app marketplace, launching a mobile application is merely the first step. The defining challenge is architecting a product that is not just functional but also inherently scalable, secure, and deeply engaging for its users. An exceptional app is never an accident; it is the direct outcome of a disciplined, strategic process grounded in proven methodologies. This guide is designed to cut through the noise, offering a comprehensive roundup of the ten most critical best practices for mobile app development.
Whether you are a startup founder meticulously planning your minimum viable product (MVP), a product manager at a growing SME looking to scale, or an enterprise CTO spearheading a digital transformation, these insights will form your essential blueprint. Our focus is on providing specific, actionable strategies that turn ambitious ideas into high-performance, market-ready digital products.
This listicle moves beyond generic advice to provide a clear, prioritized framework for success. We will cover a spectrum of essential topics, including:
- Foundational choices like mobile-first design and API-first architecture.
- Process optimizations through agile development and CI/CD pipelines.
- Crucial non-functional requirements such as performance monitoring, robust security, and automated testing.
- Growth-oriented strategies involving user experience (UX) research, analytics integration, and effective localization.
By adhering to these principles, your team can mitigate common development pitfalls, accelerate time-to-market, and build a product that not only meets but exceeds user expectations, ensuring a lasting impact. Let's dive into the core practices that separate successful apps from the rest.
1. Mobile-First Design Architecture
Mobile-first design is a strategic approach that inverts the traditional design process. Instead of creating a complex desktop application and then stripping it down for mobile, you start by designing for the smallest screen first. This methodology forces you to prioritize core content and functionality, ensuring a seamless, high-performance experience on the devices your users interact with most frequently.
This philosophy, championed by pioneers like Luke Wroblewski, isn't just about screen size; it's about embracing mobile constraints like touch inputs, variable connectivity, and limited processing power. By solving for these challenges first, the application scales up to tablets and desktops through progressive enhancement, adding features and complexity as screen real estate and resources increase. This is one of the foundational best practices for mobile app development because it aligns directly with modern user behavior.
Why It's a Best Practice
Adopting a mobile-first architecture leads to a leaner, more focused product. The constraints of a small screen compel you to eliminate clutter and concentrate on what truly matters to the user, resulting in a more intuitive UX. Companies like Instagram built their entire empire on this principle, launching exclusively on mobile to perfect the core user journey before considering other platforms. Google's shift to mobile-first indexing further underscores this importance, as it now prioritizes the mobile version of a site for ranking and indexing.
How to Implement It
- Prioritize Core Features: Begin by identifying the single most important action a user needs to accomplish. Build the entire initial wireframe around this core functionality, ensuring it's effortless on a small screen.
- Design for Touch: Use large, easily tappable buttons and interactive elements. Ensure there is adequate spacing between targets to prevent accidental taps.
- Prototype on Mobile: Start wireframing and prototyping exclusively on mobile layouts. Use actual devices for testing, not just browser emulators, to get a true feel for the user experience.
- Optimize Performance: Mobile users have less patience for slow load times. Focus on optimizing images, minimizing code, and leveraging browser caching from the very beginning.
2. Cross-Platform Development Frameworks
Cross-platform development frameworks offer a powerful alternative to building separate native applications for iOS and Android. Using technologies like React Native, Flutter, or Xamarin, developers can write a single, unified codebase that compiles and runs on multiple operating systems. This approach significantly reduces development time and costs by eliminating the need to manage two distinct codebases, making it one of the most efficient best practices for mobile app development.

Pioneered by tech giants like Facebook (React Native) and Google (Flutter), these frameworks bridge the gap between web technologies and native performance. They allow teams to share logic, UI components, and business rules across platforms, accelerating the product lifecycle from initial build to ongoing maintenance. This unified strategy is crucial for startups and enterprises aiming for rapid market entry and consistent user experiences across all devices.
Why It's a Best Practice
Adopting a cross-platform framework is a strategic move to optimize resource allocation and accelerate time-to-market. It allows a smaller team to support both iOS and Android, ensuring feature parity and a consistent brand identity. Companies like Shopify have leveraged React Native to power their mobile commerce apps, enabling them to innovate quickly. Similarly, Google uses its own Flutter framework for major apps like Google Pay, proving that near-native performance is achievable. For a deeper dive, you can explore more about cross-platform mobile app development.
How to Implement It
- Evaluate Framework Maturity: Before committing, assess the ecosystem of your chosen framework. Consider its community support, available libraries, and long-term roadmap. For instance, in the React Native ecosystem, a detailed comparison of Expo and React Native can help you select the right tooling for your project's specific needs.
- Plan for Native Code: Expect that 10-20% of your application will require platform-specific code to access native APIs or achieve performance-critical functionality. Plan for this by structuring your project to easily accommodate native modules.
- Optimize Performance-Critical Features: Use native modules strategically for features that demand high performance, such as complex animations, heavy data processing, or background tasks. This hybrid approach gives you the best of both worlds.
- Automate Cross-Platform Testing: Implement a robust CI/CD pipeline that automatically builds and tests your application on both iOS and Android simulators and real devices. This ensures that a code change doesn't inadvertently break one platform.
3. Agile Development and Sprint Cycles
Agile development is an iterative approach to project management and software development that helps teams deliver value to their customers faster and with fewer headaches. Instead of betting everything on a single, high-stakes launch, an agile team delivers work in small, digestible increments. This methodology prioritizes collaboration, customer feedback, and the ability to adapt to change on the fly.
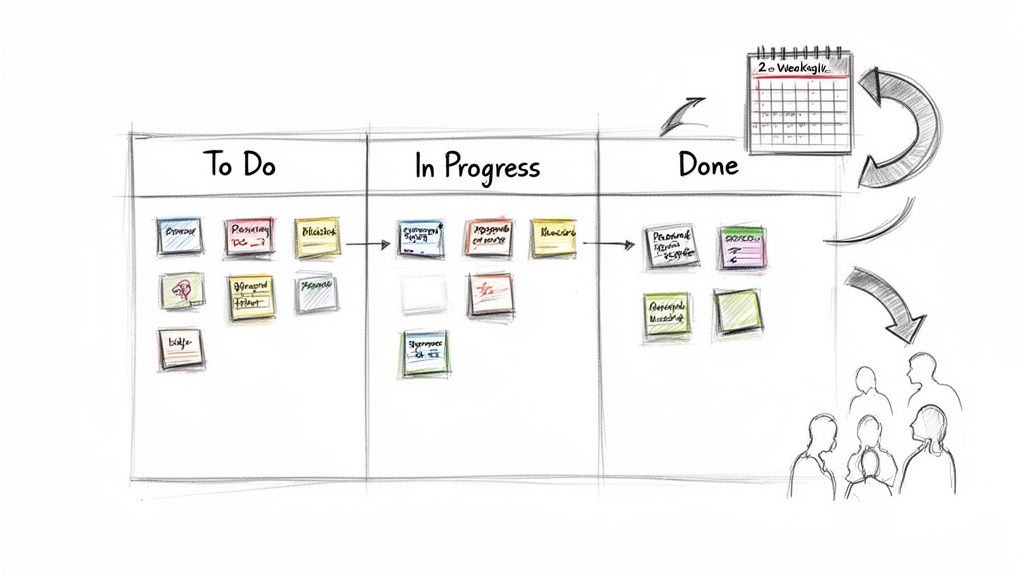
Pioneered by visionaries like Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland, agile frameworks like Scrum break down large, complex projects into manageable, time-boxed periods called sprints, which typically last one to four weeks. This structure ensures that development is transparent, predictable, and aligned with user needs. Embracing this workflow is one of the most impactful best practices for mobile app development, as it allows teams to pivot quickly based on real-world market feedback rather than outdated assumptions.
Why It's a Best Practice
Adopting an agile methodology dramatically reduces the risk of building the wrong product. By delivering a functional piece of the app every few weeks, teams can gather user feedback early and often, ensuring the final product truly solves a real problem. Companies like Spotify have famously used an agile-inspired squad model to foster autonomy and accelerate innovation, while Uber's rapid iteration cycles allowed it to scale features and adapt to new markets with incredible speed. This continuous feedback loop is critical in the fast-moving mobile landscape.
How to Implement It
- Define a Clear "Definition of Done": Establish explicit criteria for when a user story or task is considered complete. This eliminates ambiguity and ensures consistent quality across all deliverables.
- Use Backlog Management Tools: Leverage platforms like Jira, Asana, or Monday.com to organize your product backlog, plan sprints, and track progress transparently.
- Keep Sprint Goals Focused: Each sprint should have a single, achievable goal. Avoid overloading the team with unrelated tasks, which can dilute focus and reduce the chances of a successful delivery.
- Conduct Action-Oriented Retrospectives: After each sprint, hold a retrospective meeting focused on identifying what went well, what didn't, and creating actionable steps for process improvement in the next cycle.
- Balance New Features with Technical Debt: Consciously allocate a portion of each sprint to address technical debt. This prevents the codebase from deteriorating over time and ensures long-term stability and performance.
4. API-First Architecture and RESTful Design
API-first architecture is a development strategy where the application programming interface (API) is treated as a primary product. Instead of building the backend and then creating an API for the mobile app to consume, you design, document, and mock the API first. This approach establishes a clear contract that both frontend (mobile) and backend teams can develop against simultaneously, accelerating the entire development lifecycle.
This methodology decouples services and clients, making systems more scalable and maintainable. It relies heavily on RESTful principles, an architectural style defined by Roy Fielding that uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), clear resource URLs, and status codes to create predictable and stateless communication. Adopting this is one of the most critical best practices for mobile app development because it ensures the backend can support any client, not just the initial mobile app.
Why It's a Best Practice
An API-first approach reduces dependencies between teams, allowing parallel development and faster iteration. It forces clear communication and planning upfront, resulting in a more robust, reusable, and well-documented backend. The Stripe API is a gold standard, offering an incredibly consistent and developer-friendly interface that has become a cornerstone of its business. Similarly, the well-documented APIs from GitHub and Twilio demonstrate how a strong API can foster an entire ecosystem of third-party integrations.
How to Implement It
- Define with OpenAPI: Use specifications like OpenAPI (formerly Swagger) to design and document your API contract before writing any code. This creates a single source of truth for all teams.
- Version from Day One: Implement API versioning in the URL (e.g.,
/api/v1/users) from the very beginning. This allows you to introduce breaking changes in future versions without disrupting existing mobile clients. - Use Standard HTTP Practices: Adhere strictly to RESTful principles. Use appropriate HTTP verbs for actions, standard status codes for responses (e.g., 200 OK, 404 Not Found, 500 Server Error), and design predictable resource URLs.
- Plan for Scale: Design endpoints with pagination for large datasets to prevent performance bottlenecks. Implement rate limiting and security measures using an API Gateway to protect your backend services.
5. Automated Testing, Quality Assurance and CI/CD Pipelines
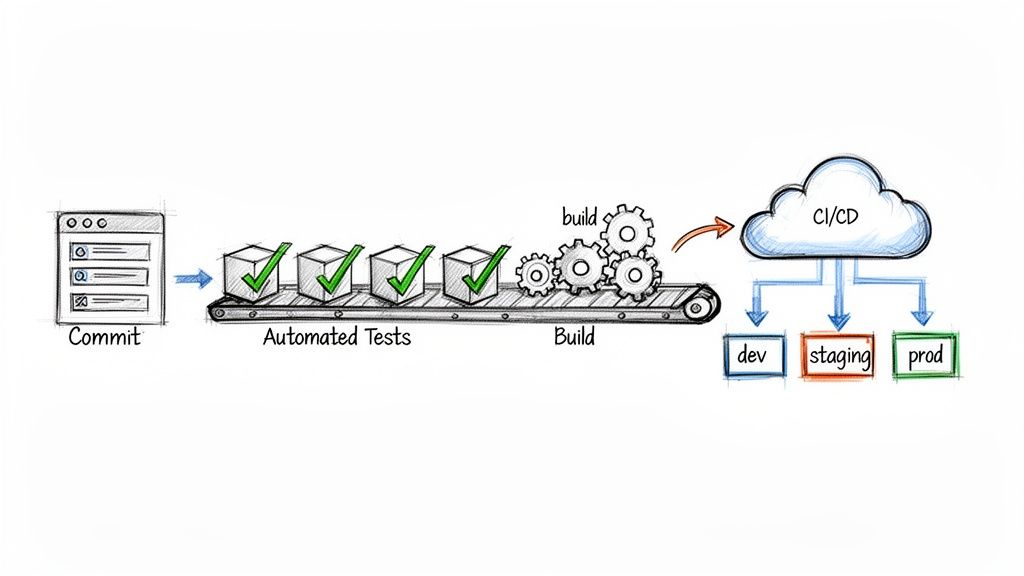
Automated testing and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines form the backbone of modern, high-velocity mobile development. This practice involves creating a fully automated workflow that builds, tests, and deploys your mobile application. By integrating automated checks at every stage, from unit tests on individual code components to full end-to-end user interface tests, teams can catch bugs early, prevent regressions, and release updates with speed and confidence.
This approach shifts quality assurance from a manual, end-of-cycle bottleneck to an integrated, continuous process. Pioneers like Jez Humble and David Farley established the principles of CI/CD, which tech giants like Amazon and Spotify have famously used to achieve thousands of deployments per day. This methodology is one of the most critical best practices for mobile app development because it enables both stability and agility, allowing teams to deliver value to users faster and more reliably.
Why It's a Best Practice
Implementing a robust automated testing and CI/CD pipeline drastically reduces the risk of human error and frees up developers from repetitive manual tasks. It ensures that every code change is automatically verified against a suite of tests, providing immediate feedback. This creates a safety net that encourages refactoring and innovation, as developers know that any breaking changes will be caught instantly. The result is a higher-quality product, a more efficient development cycle, and the ability to respond to market changes with remarkable speed.
How to Implement It
- Follow the Testing Pyramid: Structure your tests according to Google’s model: a large base of fast unit tests (around 70%), a smaller layer of integration tests (20%), and a very small top layer of slow, end-to-end UI tests (10%).
- Integrate into CI/CD Platforms: Use tools like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, or CircleCI to automatically trigger your test suite whenever new code is committed.
- Automate Builds and Releases: Automate the entire build, signing, and provisioning process for both iOS and Android. This ensures consistent and repeatable deployments to app stores.
- Prioritize Critical Paths: Begin by writing automated tests for the most critical user journeys, such as login, checkout, or core feature interactions, to maximize impact.
- Use Mocking and Stubbing: Isolate components under test by using mocks and stubs for external dependencies like APIs or databases, making tests faster and more reliable.
6. Performance Optimization and App Monitoring
Performance optimization is the practice of methodically improving an app's responsiveness, speed, and resource efficiency. It involves reducing app size, minimizing load times, and optimizing memory and CPU usage to ensure a smooth, lag-free experience. Coupled with continuous monitoring, which captures real-world metrics, this practice allows development teams to detect, diagnose, and resolve performance issues proactively before they impact users.
In today's competitive landscape, performance is a feature, not an afterthought. Users expect instant responses and will quickly abandon an app that is slow, buggy, or drains their battery. This proactive approach to performance management is one of the most critical best practices for mobile app development, directly influencing user retention, engagement, and conversion rates.
Why It's a Best Practice
A high-performing application is crucial for user satisfaction and business success. Slow performance is a leading cause of app uninstalls. By continuously optimizing and monitoring, you prevent user churn, improve your app store ratings, and enhance your brand's reputation. For example, Grab's focused optimization for low-end Android devices in Southeast Asia was key to its market dominance, ensuring the app remained usable and fast even on less powerful hardware and slower networks. Similarly, Facebook developed the Hermes JavaScript engine specifically to improve the startup time and performance of React Native apps.
How to Implement It
- Utilize APM Tools: Integrate Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools like New Relic, DataDog, or Firebase Performance Monitoring to gain real-time insights into your app's behavior in the wild.
- Implement Proactive Crash Reporting: Use services like Sentry or Rollbar to immediately capture and analyze crash reports and exceptions, allowing you to fix bugs before a majority of users are affected.
- Profile Your App Regularly: Use native profiling tools like Android Profiler and Xcode's Instruments to identify memory leaks, CPU bottlenecks, and rendering issues during the development cycle.
- Optimize Assets and Delivery: Compress images with tools like TinyPNG, implement progressive or lazy loading for content, and use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to deliver static assets quickly.
- Set Performance Budgets: Define clear performance metrics (e.g., startup time under 2 seconds, frame rate above 50 fps) and integrate checks into your CI/CD pipeline to prevent regressions.
7. Security Best Practices and Data Protection
Security is not an optional feature but a foundational pillar of mobile app development. It involves a multi-layered strategy to protect user data, secure communications, and defend against malicious attacks. This encompasses everything from encrypting data at rest and in transit to implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms, all while adhering to critical regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
A comprehensive security posture goes beyond just writing secure code. It means adopting a security-first mindset throughout the entire development lifecycle, from initial design to post-launch maintenance. This proactive approach, often referred to as a "shift-left" strategy, integrates security checks early and often, preventing costly vulnerabilities later. This is one of the most critical best practices for mobile app development, as a single breach can irreparably damage user trust and brand reputation.
Why It's a Best Practice
In an era of frequent data breaches, users are more privacy-conscious than ever. Implementing strong security measures is a direct signal that you value and protect their information, building essential trust. Companies like Signal have built their entire brand on the promise of end-to-end encryption and user privacy. Moreover, failing to comply with data protection regulations can result in severe financial penalties and legal action, making robust security a non-negotiable business requirement.
How to Implement It
- Secure Data Handling: Encrypt all sensitive data both in transit using HTTPS/TLS and at rest using native secure storage like Android's KeyStore and iOS's Keychain. Never store sensitive information like passwords or API keys in plaintext.
- Fortify API Communications: Use certificate pinning to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks. Implement rate limiting and throttling on your APIs to protect against brute-force and denial-of-service attacks.
- Follow Established Guidelines: Adhere to the OWASP Mobile Application Security Verification Standard (MASVS). This provides a clear framework for building and testing secure mobile applications.
- Automate and Test: Integrate automated security scanning tools (like Snyk) into your CI/CD pipeline to catch vulnerabilities early. For a deeper analysis of this proactive approach, you can explore the principles of shift-left security. Conduct regular third-party penetration tests to identify and remediate weaknesses.
8. User Experience (UX) Research and Testing
User Experience (UX) research is the systematic investigation of users and their requirements to add context and insight into the design process. Rather than building based on assumptions, this practice involves directly engaging with your target audience through methods like interviews, surveys, and usability testing. It ensures the final product is not just functional but also intuitive, valuable, and enjoyable to use.
This approach, championed by pioneers like Don Norman and the Nielsen Norman Group, treats development as a collaborative process with the end-user. By continuously gathering feedback and validating design choices, you transform guesswork into data-driven decision-making. This iterative cycle of research, prototyping, and testing is a cornerstone of modern best practices for mobile app development, as it directly aligns product features with genuine user needs and business goals.
Why It's a Best Practice
Integrating UX research and testing mitigates the single greatest risk in product development: building something nobody wants. It provides direct insight into user pain points, behaviors, and motivations, allowing you to create solutions that truly resonate. Airbnb, for example, extensively used user research to understand host and guest anxieties, leading to features like verified profiles and secure messaging that were critical to building trust and driving growth. This process saves significant time and resources by catching usability issues before a single line of code is written.
How to Implement It
- Create User Personas: Synthesize research data from interviews and surveys to create detailed personas representing your key user segments. Use these to guide design and feature prioritization.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Use tools like UserTesting or Maze to run moderated or unmoderated tests on your prototypes. Observe how real users interact with your app to identify points of friction. For a deeper dive into effective evaluation, explore these usability testing methods and find the right fit for your project.
- Implement A/B Testing: For critical user flows like onboarding or checkout, run A/B tests to compare different design variations and identify which one performs better against key metrics.
- Gather Continuous Feedback: Use in-app surveys, feedback forms, and analytics tools like Hotjar to monitor user behavior and collect qualitative feedback on an ongoing basis after launch.
9. Localization and Internationalization (i18n/L10n)
Internationalization (i18n) is the process of designing and developing an application so it can be easily adapted to various languages and regions without engineering changes. Localization (L10n) is the subsequent process of adapting the internationalized app for a specific region by adding locale-specific components and translating text. Building this capability into your app's architecture from the outset is a critical best practice for mobile app development, enabling scalable global growth.
This two-step approach ensures that expanding into new markets is a matter of adding new resource files, not re-engineering the core product. It transforms your app from a single-market solution into a globally ready platform. Companies like WhatsApp, which supports over 60 languages, and Netflix, offering extensive subtitle and dubbing options, have demonstrated how effective L10n can be in achieving worldwide user adoption and market penetration.
Why It's a Best Practice
Implementing i18n and L10n significantly enhances user experience and engagement by communicating with users in their native language and cultural context. This approach broadens your app's total addressable market, unlocking new revenue streams and providing a substantial competitive advantage. By planning for global audiences from day one, you reduce future development costs and accelerate time-to-market when you decide to expand, making your app more appealing to a diverse, international user base.
How to Implement It
- Externalize Strings: Never hardcode user-facing text. Store all strings in resource files (e.g.,
strings.xmlin Android,Localizable.stringsin iOS) separated by language. - Use i18n Libraries: Leverage established libraries like
i18nextor native platform frameworks to manage translations, plurals, and formatting. - Plan for UI/UX Variations: Design flexible layouts that can accommodate text expansion. For example, German text can be up to 35% longer than English. Also, test Right-to-Left (RTL) languages like Arabic and Hebrew early.
- Manage Translations Systematically: Use a translation management system like Lokalise or Crowdin to streamline the localization workflow with translators.
- Handle Locale-Specific Formats: Ensure that dates, times, numbers, and currencies are formatted correctly according to the user's regional settings, not a hardcoded standard.
10. User Feedback Loops and Analytics Implementation
Launching an app without a robust system for feedback and analytics is like navigating without a map. User feedback loops and analytics implementation form a symbiotic relationship that allows you to understand exactly how people interact with your app, identify pain points, and make data-driven decisions. This practice moves product development from guesswork to a scientific process based on real user behavior and qualitative insights.
This involves integrating powerful analytics tools to track quantitative metrics like daily active users (DAU), retention rates, and conversion funnels, while simultaneously using in-app tools to gather qualitative feedback. This combination provides a complete picture of the user experience, revealing not just what is happening, but why it is happening. This continuous flow of information is a cornerstone of agile development and one of the most critical best practices for mobile app development.
Why It's a Best Practice
This approach enables product teams to iterate with confidence. Instead of relying on assumptions, you can validate hypotheses with hard data. For example, Dropbox famously used data from their onboarding funnel to identify friction points, leading to targeted improvements that significantly boosted user activation. Similarly, Slack continuously analyzes feature adoption metrics to prioritize its development roadmap, ensuring resources are invested in what users truly value. This data-driven culture minimizes wasted effort and maximizes user satisfaction and retention.
How to Implement It
- Define Core Metrics: Before writing a single line of tracking code, identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your business goals. These might include retention, lifetime value (LTV), or task completion rates.
- Integrate Analytics Tools: Implement a comprehensive analytics platform like Firebase Analytics, Amplitude, or Mixpanel. Set up event tracking for all critical user actions and funnels, such as registration, purchase, or feature usage.
- Establish Feedback Channels: Use tools like Intercom or Apptentive to enable in-app surveys, ratings prompts, and direct user messaging. This makes it easy for users to provide feedback without leaving the app.
- Correlate Data: Don't analyze quantitative and qualitative data in silos. When analytics show a drop-off in a specific user flow, look at corresponding user feedback from that segment to understand the root cause.
- Respect User Privacy: Be transparent about the data you collect and obtain proper consent. Adhere strictly to regulations like GDPR and CCPA to build and maintain user trust.
Comparison of 10 Mobile App Development Best Practices
| Approach | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | ⭐ Expected Outcomes | 📊 Ideal Use Cases | 💡 Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile-First Design Architecture | Moderate — requires design discipline and responsive patterns | Low–Medium — designers, device testing, performance tooling | High — improved mobile performance & engagement | Consumer mobile apps; limited-bandwidth markets; startups | Progressive enhancement, faster loads, better conversions |
| Cross-Platform Development Frameworks | Moderate — framework paradigms + occasional native bridges | Medium — framework-skilled devs, some native modules, CI/CD | High — faster multi-platform delivery with near‑native UX | MVPs, SMEs needing iOS + Android quickly | Single codebase, lower cost, rapid iteration |
| Agile Development and Sprint Cycles | Low–Medium — process adoption and ceremony overhead | Low — team training and collaboration tools; high client involvement | High — faster feedback, reduced project risk | Projects with changing requirements; iterative products | Rapid iteration, transparency, frequent value delivery |
| API-First Architecture and RESTful Design | Moderate — upfront API design, versioning, contracts | Medium — API design skills, documentation and gateway tools | High — parallel dev, maintainable and scalable backends | Multi-client platforms, third‑party integration scenarios | Clear contracts, easier testing, future-proof clients |
| Automated Testing, QA and CI/CD Pipelines | High — extensive setup and ongoing maintenance | High — testing/DevOps expertise, CI infrastructure, tooling | Very High — fewer regressions, reliable frequent releases | Enterprise systems, high-release-frequency products | Early bug detection, consistent deployments, rollback safety |
| Performance Optimization and App Monitoring | Medium–High — continuous profiling and tuning | Medium — APM tools, profiling, monitoring costs | High — improved retention, lower infrastructure costs | Performance‑sensitive apps, large user bases, low‑end devices | Better UX, proactive issue detection, cost savings |
| Security Best Practices and Data Protection | High — complex security measures and compliance work | High — security expertise, audits, tooling, maintenance | High — user trust, reduced breach and legal risk | Finance, healthcare, enterprise apps handling sensitive data | Strong trust, regulatory compliance, breach prevention |
| UX Research and Testing | Medium — planning, recruitment, iterative validation | Medium — researchers, testing participants, prototyping tools | High — better product‑market fit and conversion rates | New features, onboarding flows, redesigns | Data‑driven design, reduced wasted development |
| Localization and Internationalization (i18n/L10n) | Medium — architecture for locale support; ongoing L10n effort | Medium–High — translators, QA, i18n tooling, testing | High — expanded markets and higher regional engagement | Global rollouts, multilingual user bases | Access new markets, improved local conversion rates |
| User Feedback Loops and Analytics Implementation | Medium — instrumentation, event modeling, privacy controls | Medium — analytics platforms, analysts, dashboards | High — evidence‑based decisions and prioritized roadmaps | Growth teams, retention optimization, feature validation | Measurable impact, faster prioritization, reduced feature waste |
Build Better, Faster, and Smarter
Navigating the complex journey of mobile app development requires more than just a brilliant idea. It demands a disciplined, strategic approach grounded in proven methodologies. Throughout this guide, we've explored ten foundational pillars that separate successful, high-growth applications from those that falter. From establishing a mobile-first design architecture to implementing robust user feedback loops, each practice represents a critical piece of the puzzle. Adhering to these principles is the most reliable way to ensure you build a product that is not only functional but also scalable, secure, and truly resonant with your target audience.
The journey from concept to launch is a marathon, not a sprint, and these best practices for mobile app development act as your strategic roadmap. They are interconnected systems that build upon one another, creating a powerful flywheel of efficiency and quality. For example, an API-first architecture simplifies the integration of new features, while an Agile development framework allows you to pivot and adapt based on real-time feedback. When you combine this with a strong CI/CD pipeline, you're not just building features; you're building a resilient, automated product engine that delivers value to users continuously and reliably.
From Principles to Production: Your Actionable Next Steps
Mastering these concepts transforms development from a series of disjointed tasks into a cohesive, goal-oriented process. The ultimate value lies in building a sustainable product that can adapt to changing market demands and user expectations. A well-architected app with a focus on performance and security builds trust, drives user retention, and ultimately protects your brand's reputation. So, where do you begin?
Here are your immediate next steps to put these insights into action:
- Conduct a Process Audit: Review your current development lifecycle against the ten practices outlined here. Identify the most significant gaps. Are you neglecting automated testing? Is your security posture an afterthought? Prioritize the area that poses the most risk or offers the greatest potential for improvement.
- Prioritize User-Centricity: If you haven't already, make UX research and testing a non-negotiable part of your next sprint. Even small-scale usability tests can uncover critical insights that save significant rework down the line. Start collecting and analyzing user feedback immediately.
- Future-Proof Your Architecture: Evaluate your current technology stack. Is it built for global scale with localization and internationalization in mind? Are you leveraging a modern cross-platform framework to maximize reach and minimize maintenance overhead? Making strategic architectural decisions today prevents costly technical debt tomorrow.
Your Partner in Building Exceptional Digital Products
Adopting these best practices for mobile app development is a commitment to excellence. It’s about more than just checking boxes; it’s about fostering a culture of quality, agility, and continuous improvement within your team. By embedding these principles into your DNA, you de-risk your project, accelerate your time to market, and build a powerful foundation for long-term growth. The result is a superior digital product that not only meets user needs but delights them, creating loyal advocates for your brand.
The path to building a market-leading application can be challenging, but you don't have to walk it alone. If your organization is ready to elevate its development capabilities and transform a vision into a high-performance reality, expert guidance can make all the difference. By partnering with a dedicated team that lives and breathes these principles, you can ensure your next project is engineered for success from day one.