Enterprise Application Development Services: Build Scalable Solutions Fast

Think of enterprise application development services as the master architects for your company's digital infrastructure. They go far beyond off-the-shelf software, creating custom-built platforms that act as the central nervous system for your entire operation. It's about ditching the clunky, one-size-fits-all tools and building something that’s a perfect fit for how you actually work.
Building Your Digital Headquarters
Could you imagine running a global logistics empire on a bunch of spreadsheets? It would be pure chaos—inefficient, error-prone, and completely unscalable. This is precisely the kind of problem enterprise application development services are designed to solve. They replace fragmented, manual work with slick, integrated systems built for serious performance.
These aren't just simple mobile apps. We're talking about sophisticated software solutions that become the operational backbone of the business, aligning perfectly with your specific workflows and long-term goals.
From Disjointed Tools to a Unified System
The real magic of custom enterprise development is creating a single source of truth for the entire company. It’s about connecting all the dots—linking finance to operations, sales to the supply chain, and HR to project management—so everyone is on the same page, working from the same data.
The main objectives here are clear:
- Deep Integration: Weaving together all your existing systems, from old-school legacy databases to modern cloud services, to get data flowing freely where it needs to go.
- Enhanced Security: Locking down sensitive corporate information with tough security measures that meet today’s demanding compliance standards.
- Unmatched Scalability: Constructing applications on a framework that can handle growth, effortlessly managing more users and bigger data volumes as your business expands.
An effective enterprise application doesn't just automate tasks; it fundamentally transforms how a business operates. It turns fragmented data points into actionable intelligence, driving smarter decisions at every level of the organization.
To get a full picture of what’s possible today, you need to understand concepts like what is a Digital Experience Platform (DXP). A DXP is a great example of this unified approach, as it centralizes how a company engages with customers across every single touchpoint.
In the end, these services deliver much more than just lines of code. They provide a genuine competitive edge by engineering a well-oiled operational machine that turns your biggest challenges into opportunities for efficiency and growth.
Exploring the Types of Enterprise Applications
To really get what enterprise application development services are all about, you first have to understand the software they create. These aren't your everyday apps. They are the operational backbone of a company, with each one built to tackle a specific, high-stakes business challenge.
Imagine a large business is like a complex machine. Each type of enterprise application is a specialized gear, designed to make one part of the machine run perfectly. The real magic happens when you get all these gears to mesh together, creating a powerful, unified engine that moves the whole company forward.
Let's break down some of the most common types.
Key Types of Enterprise Applications and Their Functions
This table provides a quick look at the most common enterprise applications, what they do, their essential features, and who uses them the most.
| Application Type | Primary Purpose | Core Features | Primary Business Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) | To unify and manage core business processes from a single system. | Financial management, procurement, manufacturing, supply chain, HR modules. | Operations, Finance, HR, Manufacturing |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | To manage and analyze all customer interactions throughout the lifecycle. | Lead tracking, sales automation, contact management, marketing campaigns. | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service |
| Supply Chain Management (SCM) | To oversee the end-to-end flow of goods, from sourcing to delivery. | Inventory management, logistics, order fulfillment, supplier collaboration. | Logistics, Procurement, Operations |
| Business Intelligence (BI) | To analyze data and present actionable insights for decision-making. | Data visualization, reporting, dashboards, performance metrics (KPIs). | Executive Leadership, Analysts, Department Heads |
| Human Resource Management (HRM) | To manage all aspects of the employee lifecycle. | Payroll, recruiting, onboarding, benefits administration, performance tracking. | Human Resources, Management |
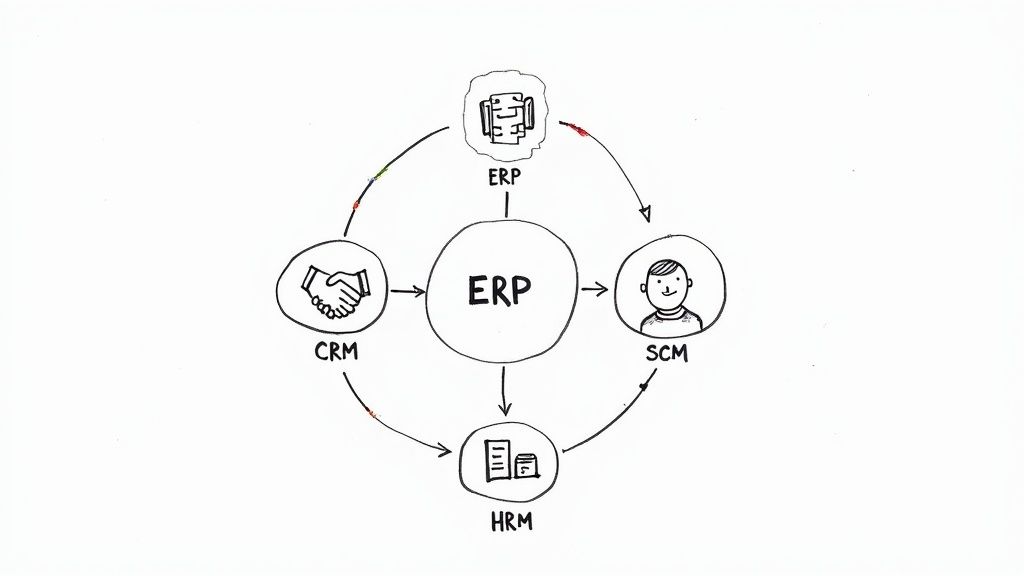
While this table gives you the highlights, it's worth digging into the big three—ERP, CRM, and SCM—to see how they really function.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Think of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system as the central nervous system of a company. It pulls together all the critical business functions—finance, manufacturing, HR, the supply chain—into one integrated platform with a shared database.
Without an ERP, departments often operate in silos with their own disconnected software. But with an ERP, everyone works from the same playbook. For instance, when a salesperson logs a new order, the system can automatically check inventory levels, schedule production, and notify the accounting team to prepare an invoice. This seamless flow of information gets rid of manual data entry and makes the whole operation run smoother.
Because they are so fundamental, ERP systems are a huge part of the enterprise software market. Projections show ERPs are set to capture a 30.6% market share by 2025. This is especially true in North America, which is expected to hold a 41.8% regional share, driving a huge demand for custom ERPs built for complex business needs. You can dig into the numbers yourself in this detailed enterprise application market report.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Platforms
If an ERP looks inward at a company's operations, a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform looks outward. It’s designed to manage every single interaction a company has with its customers and prospects. This is way more than just a fancy digital address book; it’s a strategic powerhouse for your sales, marketing, and service teams.
A good CRM maps out the entire customer journey, from the first time someone sees an ad all the way through to the sale and any follow-up support. This gives you a 360-degree view, helping you turn leads into customers, personalize your communication, and keep people coming back. For example, a customer service rep can instantly pull up a caller's full purchase history, which helps them solve problems way faster.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) Software
For any business that makes or moves physical products, Supply Chain Management (SCM) software is non-negotiable. SCM systems give you a bird's-eye view of your entire supply chain, from the moment you source raw materials to when the finished product lands on a customer's doorstep.
These applications are all about logistics. They help companies manage inventory, predict demand, and coordinate with suppliers and shipping partners. A well-implemented SCM can spot a potential shipping delay before it happens, find ways to cut transportation costs, and make sure you're never out of stock.
An integrated enterprise application ecosystem is no longer a luxury; it's a competitive necessity. It transforms data from a scattered liability into a strategic asset, empowering leaders to make smarter, faster decisions.
Other Key Enterprise Applications
Beyond those big three, enterprise application development services also build other critical systems:
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: These tools are the brains of the operation. They plug into your other systems (like your ERP and CRM), pull out massive amounts of data, and turn it all into easy-to-understand reports and dashboards. This helps executives spot trends and make decisions based on hard data, not just gut feelings.
- Human Resource Management (HRM) Systems: An HRM system handles everything related to your people. It automates and centralizes core HR tasks like recruiting, onboarding, payroll, benefits, and performance reviews. This not only makes things more efficient but also frees up your HR team to focus on bigger-picture goals like talent development.
Each of these systems has its own job to do, but their real value is unlocked when they talk to each other, creating a single, cohesive digital environment that supports every part of the business.
Mapping Your Custom Development Journey
Building a custom enterprise application isn’t a single event; it's a structured journey. It follows a proven lifecycle designed to turn an abstract business problem into a powerful, working tool. Each phase builds on the last, ensuring the final product is secure, reliable, and perfectly aligned with what your organization actually needs.
This end-to-end process is known as the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), and it’s the roadmap that guides a project from a simple idea to long-term success. Understanding these stages is critical for anyone involved in an enterprise application development services project.
To keep things running smoothly, it's always a good idea to follow established Software Development Life Cycle best practices.
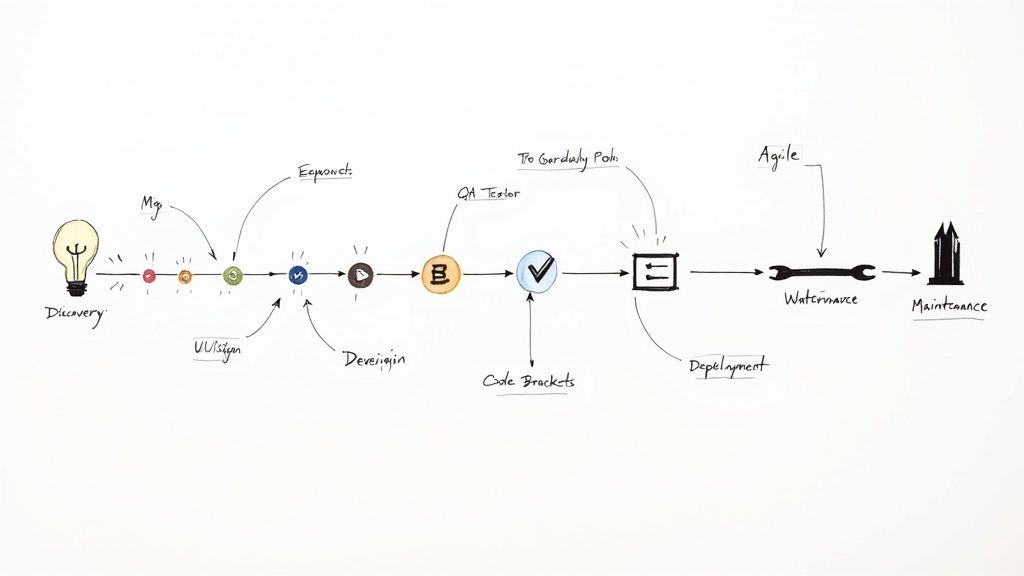
The Core Stages of Development
The journey from concept to reality breaks down into six distinct stages. Every step demands close collaboration between your team and your development partner to make sure the project stays on track and delivers real value. For a more detailed look, you can explore our complete guide on the enterprise software development process.
Discovery and Strategy: This is where we figure out the "why." It all starts with a deep dive into your business requirements, interviews with key stakeholders, and setting clear objectives and KPIs. The result is a detailed project scope and technical spec document—the blueprint for everything that comes next.
UI/UX Design: Before a single line of code is written, we have to nail the user experience. UI (User Interface) designers focus on the visual layout, while UX (User Experience) designers map out how users will interact with the app. The goal is to create something so intuitive and efficient that people actually want to use it. Good design drives adoption.
Development and Coding: Here’s where the blueprint becomes a reality. Developers get to work writing the code for both the front-end (what users see) and the back-end (the servers, databases, and application logic). This is the heavy-lifting phase that turns all the plans into a functional piece of software.
Quality Assurance (QA) Testing: In enterprise development, rigorous testing is non-negotiable. The QA team methodically hunts for bugs, performance bottlenecks, and security holes. This involves everything from functional and integration testing to User Acceptance Testing (UAT), ensuring the app works exactly as intended in the real world.
Deployment: Once the application passes every test with flying colors, it’s time to go live. This stage involves moving the code to the production environment where your team can finally start using it. A well-planned deployment ensures a smooth transition with minimal disruption to your business.
Maintenance and Support: The work doesn't stop at launch. Ongoing maintenance is essential for fixing any bugs that pop up, applying security patches, and rolling out performance updates. This phase guarantees the application stays reliable and secure as your business needs change over time.
Choosing Your Building Philosophy: Waterfall vs. Agile
Just as important as what you build is how you build it. The two most common methodologies in enterprise application development are Waterfall and Agile, and they represent two very different philosophies.
Think of Waterfall as building a skyscraper: the entire blueprint is finalized upfront, and construction proceeds in a fixed, linear sequence from foundation to rooftop. Agile, in contrast, is like cultivating a garden: you plant a section, nurture it, gather feedback, and adapt your plans for the next season based on what grows best.
The Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model is the traditional, sequential approach. Each phase of the SDLC has to be 100% complete before the next one can begin.
- Pros: It’s highly structured, with clear deliverables and milestones at each stage. This makes it a solid choice for projects where the requirements are stable and well-understood from the start.
- Cons: Its biggest weakness is inflexibility. If you need to change something mid-project, it can be costly and difficult because you have to go all the way back to the beginning stages.
The Agile Model
Agile takes a completely different, iterative approach. The project is broken down into small, manageable cycles called "sprints." In each sprint, a small piece of functionality is designed, built, and tested, which allows for constant feedback and adaptation.
- Pros: It’s incredibly flexible and can easily handle changing requirements. Agile fosters close collaboration and delivers value to the business much faster through these small, incremental releases.
- Cons: This model requires more active involvement from stakeholders. It can also be less predictable in terms of final timelines and budget if the project scope isn't managed carefully.
Ultimately, the choice depends on your project's complexity and your company's culture. For straightforward projects with fixed requirements, Waterfall offers predictable structure. For most complex, evolving enterprise projects, Agile’s adaptability is the key to success.
Choosing the Right Technology and Architecture
The technical foundation you choose for your enterprise application will define what it can do for years to come. Picking the right technology stack and architectural pattern is a massive decision, one that directly shapes performance, scalability, and how much it will cost to maintain down the road. This isn't just a choice for the IT department; it's a strategic business decision.
Think of it this way: the technology stack is your set of building materials. Just like a builder chooses between steel, concrete, or timber based on a building's purpose, a development partner selects a stack based on your project's specific goals.
Selecting the Right Technology Stack
A technology stack is simply the combination of programming languages, frameworks, databases, and other tools used to build and run an application. There’s no single "best" stack for everyone. The right choice hinges on things like your scalability goals, what your IT infrastructure already looks like, and the specific skills of your development team.
Some popular stacks we see in the enterprise space include:
- MEAN/MERN: These JavaScript-based stacks (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular/React, Node.js) are fantastic for building fast, dynamic web applications and APIs.
- .NET: Coming from Microsoft, the .NET framework is a powerful and secure choice for complex, large-scale systems, especially if your organization is already in the Windows ecosystem.
- Java: Known for its "write once, run anywhere" philosophy and a massive community, Java is still the go-to for mission-critical applications in finance and other highly regulated industries.
Every choice involves a trade-off. One stack might get you to market faster, but another could offer better long-term scalability and security. A seasoned provider of enterprise application development services will walk you through these options to land on the perfect fit.
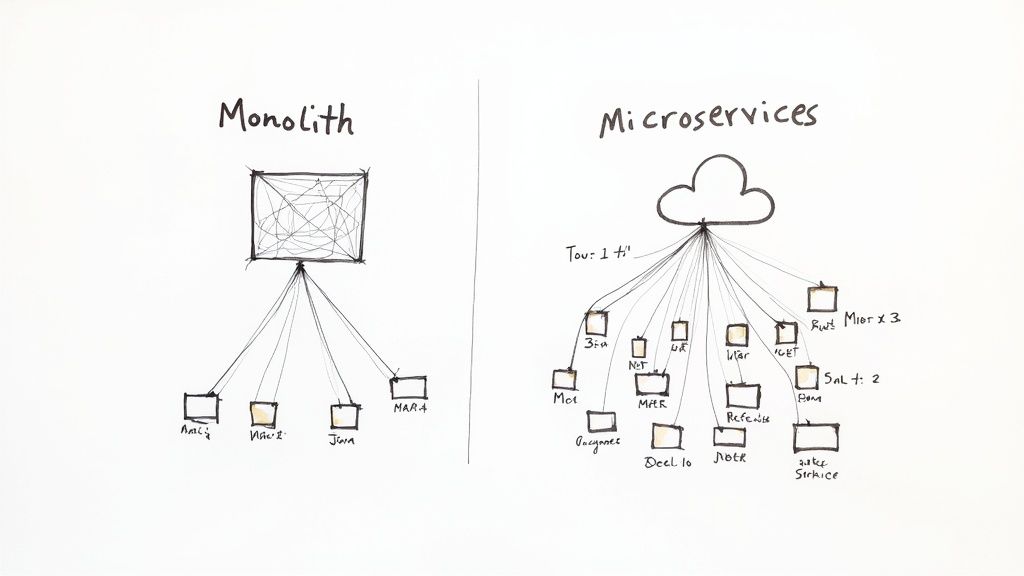
The Big Shift From Monolith to Microservices
Beyond the stack, the architectural pattern is just as crucial. This is the blueprint for how all the different parts of your application fit together and communicate. For decades, the standard was the monolithic architecture.
Imagine a single, massive department store where everything—clothing, electronics, groceries—is under one roof and run by one central system. That’s a monolith. All the code is woven together into a single, large unit. While this can be simpler to build at first, it becomes a nightmare to update, scale, or maintain as the application gets bigger. A small change in one area can unexpectedly break the entire system.
Today, the monolithic approach is giving way to a more flexible and resilient model: microservices. This architectural style structures an application as a collection of small, independent services, each responsible for a specific business capability.
Think of microservices as a modern shopping mall filled with independent, specialized boutiques. Each boutique (or service) operates on its own, has its own staff (database), and can be renovated or even replaced without shutting down the rest of the mall. For enterprise systems, this model offers some huge advantages. You can dive deeper into these powerful approaches in our guide to software architecture design patterns.
Why Microservices Future-Proof Your Investment
Moving to a microservices architecture is a strategic play to ensure your application can grow and change right along with your business. It's the foundation for building modern, cloud-native applications that are ready for whatever comes next.
The key benefits really stand out:
- Enhanced Scalability: You can scale individual services based on demand. If your payment processing service gets slammed during a sale, you can beef up just that one component without touching anything else.
- Greater Flexibility: Different services can be built using different technologies. This allows your team to use the absolute best tool for each specific job.
- Easier Maintenance: Smaller, independent codebases are much easier for developers to understand, update, and debug. This leads to faster, more reliable release cycles.
This trend toward flexible, scalable architecture goes hand-in-hand with the dominance of the cloud. In fact, cloud-based solutions have completely reshaped enterprise application development services, capturing 57% of the market share in 2024. It’s a clear sign that businesses are moving away from rigid, on-premise systems and toward the agility that only the cloud can offer. You can find more data on this trend by reading the full research on the enterprise application market.
How to Select the Right Development Partner
Choosing a partner to build your enterprise application is a monumental decision, just as critical as the technology stack you select. This isn't just about hiring a few extra developers; it's about finding a strategic ally who gets your business and can navigate the complexities of building mission-critical software. The quality of this partnership will directly shape your project's success, budget, and timeline.
Think of it this way: you wouldn't hire the cheapest contractor to build your corporate headquarters. You’d want a firm with a rock-solid reputation, a portfolio of similar high-stakes projects, and a transparent process. The same logic applies here.
Start with Technical Expertise and Industry Experience
First things first, you need to vet a potential partner's technical chops and their experience in your specific industry. A team might be amazing at building e-commerce sites, but that doesn't mean they understand the stringent compliance demands of healthcare or finance. You need a partner who already speaks your language.
When you're digging into their technical skills, look for real proof:
- Technology Stack Proficiency: Do they have battle-tested experience in the tech you need, whether it's .NET, Java, or modern JavaScript frameworks?
- Architectural Knowledge: Can they clearly explain why a microservices architecture might—or might not—be the right fit for your project? They should be able to articulate the pros and cons of different architectural patterns.
- Security Certifications: Look for credentials like ISO 27001. This isn't just a nice-to-have; it’s proof of a serious, systematic approach to information security, which is non-negotiable for any enterprise application.
A strong portfolio is your best evidence. Don't just look at a list of logos; ask for detailed case studies on projects that mirror your own in scale and complexity. This will tell you far more than any sales pitch.
Evaluate Engagement and Sourcing Models
Once you've shortlisted a few firms with the right expertise, the next step is figuring out the best way to work with them. This involves choosing an engagement model (how you'll pay) and a sourcing model (where the team is located). Each comes with its own trade-offs in cost, control, and day-to-day collaboration.
Choosing an engagement model isn't just a financial decision; it's a strategic one that defines the nature of your relationship. It determines how you collaborate, manage scope, and adapt to changes throughout the project lifecycle.
Here’s a quick rundown of the most common engagement models:
- Fixed-Price: This works well for smaller projects where the requirements are crystal clear and unlikely to change. You agree on a total cost upfront, giving you budget predictability at the expense of flexibility.
- Time & Materials (T&M): You pay for the actual hours your team works. This model is built for flexibility, making it perfect for complex, long-term projects where you expect requirements to evolve.
- Dedicated Team: In this model, you essentially hire an entire team that works only on your project. They become a true extension of your in-house staff, offering deep integration and a high degree of control.
After that, you need to think about geography—the sourcing model.
Comparing Sourcing Models for Development Partners
Where your development team is located has a huge impact on your budget, communication flow, and even cultural alignment. The right choice depends entirely on your project's needs and your team's ability to collaborate across distances.
Here's a look at how the three main sourcing models stack up against each other.
| Model | Cost Efficiency | Time Zone Overlap | Communication Ease | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onshore | Lowest | Complete | Highest | Projects needing intense, real-time collaboration and minimal cultural gaps. |
| Offshore | Highest | Limited | Challenging | Cost-sensitive projects where work can be done asynchronously with clear documentation. |
| Nearshore | Medium | Substantial | High | Companies seeking a balance of cost savings and strong collaboration without major time zone issues. |
For many businesses, nearshore staff augmentation hits a compelling sweet spot. It delivers significant cost savings compared to onshore teams while maintaining excellent time zone alignment and cultural affinity. This makes real-time collaboration feel natural and efficient, helping you sidestep the late-night calls and communication lags that often come with offshore models.
Ultimately, the glue that holds any great partnership together is communication and transparency. A top-tier partner will give you regular, honest updates, keep meticulous documentation, and make you feel like a true collaborator—not just another name on their client list. By carefully weighing technical skills, working models, and communication styles, you can find an enterprise application development services provider that will truly bring your vision to life.
Forecasting Your Project Costs and Timelines
So, what’s this actually going to cost, and when will it be ready? That's the million-dollar question, and getting it right from the start is crucial for keeping your stakeholders happy.
Unfortunately, there's no simple price list for enterprise application development services. The final numbers hinge on a handful of key factors, so a one-size-fits-all estimate just doesn't exist. But if we break down what drives the cost, we can build a much clearer picture.
Think of it like building a house. A small, simple cottage has a very different budget and construction timeline than a sprawling, multi-story mansion with a home theater and a pool. The same logic applies here—the scope and complexity of your application are the biggest factors influencing the final price tag and launch date.
Key Cost and Timeline Drivers
Several variables directly impact your project's bottom line. Getting a handle on these is the first step to smart financial planning. For a deeper dive into the mechanics of estimation, our guide on software development cost estimation methods is a great resource.
Here are the main things that move the needle:
- Application Complexity: A straightforward internal dashboard is worlds away from a massive ERP system that has to juggle intricate business rules and thousands of transactions a minute. More complexity means more cost.
- Feature Scope: How many things does the app need to do? Each new feature, screen, or user permission adds to the development time. It's simple math: more features equal more hours for design, coding, and testing.
- Third-Party Integrations: Does your new app need to talk to your old systems? Connecting to a CRM, payment processor, or ancient database always adds another layer of work and requires specialized skills.
- Technology Stack: Your choice of programming languages and frameworks matters. Some technologies demand developers with highly specialized—and often more expensive—expertise.
Sample Project Scenarios
Let's put this into perspective with a few real-world examples. A custom CRM for managing your sales team and customer interactions might take around 6-9 months to build. On the other end of the spectrum, a full-blown, custom ERP system designed to run your entire company's operations could easily stretch beyond 18 months.
The demand for these kinds of custom solutions is exploding. The market for enterprise application development jumped from $194.427 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach $278.5 billion by the end of 2025. This massive growth shows just how many businesses are betting big on custom software to stay competitive. You can discover more insights about this market expansion to see the full trend.
Remember, the initial development cost is only part of the story. To get a true picture of your investment, you must consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Beyond the upfront build, TCO includes all the ongoing expenses needed to keep your application healthy and secure. We're talking about things like server hosting, software licenses, security patches, bug fixes, and user support. Thinking about TCO from day one helps you create a realistic budget for the long haul, so you don't get hit with surprise costs down the road.
Frequently Asked Questions
It's natural to have questions when you're wading into enterprise application development. We get it. Let's clear up some of the most common ones so you can move forward with confidence.
What’s the Real Difference Between an Enterprise App and a Regular App?
The main distinctions boil down to scale, complexity, and purpose. A consumer app, like a social media or weather app, is usually built for one person at a time and does one or two things really well. Enterprise applications are a completely different beast.
These are the mission-critical systems that run your entire business. They're designed to handle complex workflows that span multiple departments, serve thousands of users at once, and integrate deeply with other core systems like your CRM or supply chain software. They demand rock-solid security and near-perfect reliability.
A good analogy is the difference between a personal sedan and a commercial airliner. Both get you from A to B, but one is designed to transport hundreds of people and tons of cargo safely and efficiently as part of a massive, interconnected network.
How Long Does Enterprise Application Development Usually Take?
There's no one-size-fits-all answer here, as the timeline depends entirely on what you're building. But we can give you some realistic ballpark figures.
- A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) or a relatively simple application can often be delivered in 4-6 months.
- A medium-complexity app with several key integrations will typically take 6-12 months from start to finish.
- A large-scale, complex system—like a custom ERP built from the ground up—can easily take 18 months or more to architect, build, and deploy properly.
Should We Build Our App In-House or Outsource?
This is a classic "build vs. buy" decision that comes down to your internal resources, long-term goals, and budget.
Building an in-house team gives you total control, but it's a massive commitment. You have to find, hire, and train specialized talent, which is not only expensive but can seriously slow you down.
Outsourcing to an experienced enterprise development partner gives you instant access to a full team of experts, established processes, and a much quicker path to launch. You get the skills you need, right when you need them, without the long-term overhead of new hires.
There’s also a great middle ground: a hybrid approach like nearshore staff augmentation. This model lets you supplement your existing team with specialized developers from a partner firm. You get the hands-on control of an in-house project combined with the flexibility and expert talent of an outsourced team.