Top 10 Web Development Trends To Watch In 2026

In a competitive market, a high-performance, secure, and engaging web presence is no longer a luxury, it's a foundational business requirement. Staying ahead requires more than just maintaining the status quo; it demands a strategic understanding of the technological shifts that define modern digital experiences. This article moves beyond generic predictions to deliver a comprehensive analysis of the most critical web development trends shaping the industry. We will dissect the technologies and methodologies that are not just gaining traction but are actively redefining how businesses build, deploy, and scale their online platforms.
This is not a surface-level overview. For each trend, we provide a detailed breakdown covering its business impact, technical implications, and practical implementation strategies. Whether you're a CTO planning your next architectural overhaul, a product manager seeking to enhance user engagement, or a startup founder aiming to build a scalable application from the ground up, this guide offers actionable intelligence. You will gain a clear understanding of concepts like AI-powered code generation, the strategic advantages of edge computing, and the agility offered by composable architectures.
We will explore ten pivotal trends, from the security imperatives of a Zero-Trust framework to the performance gains of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and the efficiency of API-first development with GraphQL. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions, prioritize your development roadmap, and align your technology stack with your long-term business objectives. By understanding these shifts now, you can build a more resilient, efficient, and future-proof digital ecosystem.
1. AI-Powered Development & Code Generation: Your New Co-Pilot
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into the software development lifecycle has shifted from a novelty to a fundamental efficiency driver. This top web development trend is no longer about futuristic concepts; it's about practical tools that augment developer capabilities, accelerate timelines, and reduce mundane tasks. AI assistants like GitHub Copilot and Tabnine act as real-time pair programmers, offering intelligent code completions, generating boilerplate code, and even suggesting entire functions based on natural language comments.
This "co-pilot" approach allows developers to focus on complex problem-solving and architectural decisions rather than getting bogged down in repetitive syntax. The impact is a significant boost in productivity, faster onboarding for new team members, and a reduction in human error.
When and Why to Use This Approach
AI-powered development is most effective for speeding up common tasks and prototyping. Use it to quickly scaffold new components, write unit tests, or translate code snippets between languages. For instance, a developer can simply write a comment like // create a React component that fetches user data from an API and displays it in a list and receive a functional code block in seconds. This allows for rapid iteration and validation of ideas, making it invaluable in agile environments.
The rise of custom ChatGPT implementations further solidifies AI's role as a powerful co-pilot in the development process, enabling teams to build bespoke assistants trained on their own codebases and internal documentation for even more relevant suggestions.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Integrate into Your IDE: Start by installing AI coding assistant extensions directly into your integrated development environment (IDE), like VS Code or JetBrains. This provides the most seamless and contextual experience.
- Be Specific with Prompts: Treat your code comments and prompts like you're instructing a junior developer. The more context and detail you provide, the more accurate and useful the AI's output will be.
- Review and Refactor: Never blindly trust AI-generated code. Always review it for security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and adherence to your project's coding standards. Use it as a first draft, not a final product.
2. Edge Computing & Serverless Architectures
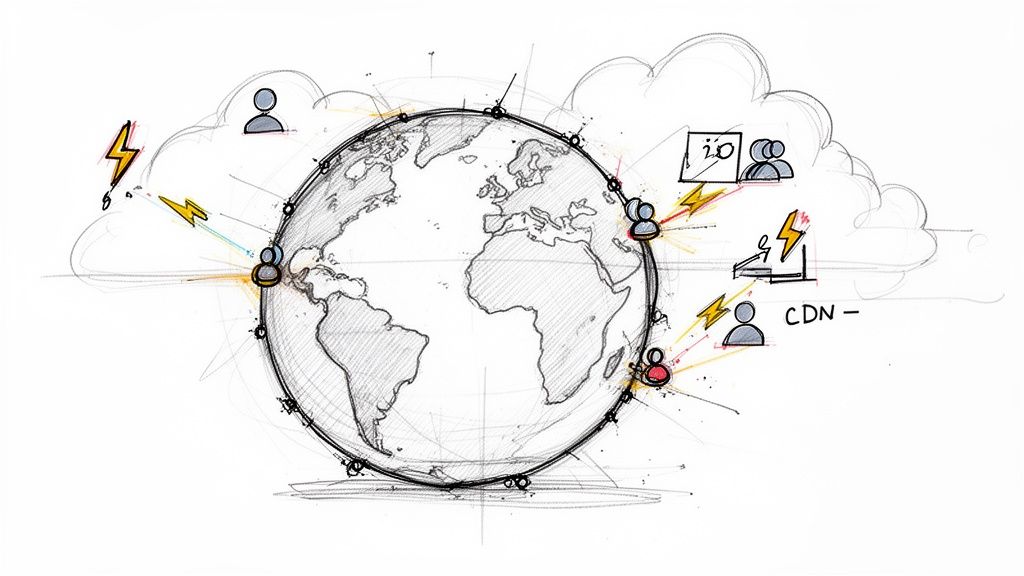
The convergence of edge computing and serverless architectures represents a paradigm shift in building fast, scalable, and globally resilient applications. This web development trend moves computation from centralized data centers to locations closer to the end-user, drastically reducing latency. Serverless functions, like those offered by Cloudflare Workers or AWS Lambda, execute on this distributed network, abstracting away all infrastructure management for developers.
This powerful combination allows code to run at the network's "edge," intercepting user requests before they even reach a traditional backend server. The result is ultra-fast dynamic content delivery, real-time API responses, and a superior user experience, regardless of the user's geographical location. This approach is becoming a cornerstone for modern, high-performance web applications.
When and Why to Use This Approach
This architecture is ideal for applications requiring minimal latency and global reach. Use it for tasks like A/B testing, API authentication, real-time personalization, or serving dynamic content that needs to be generated on the fly. For example, an e-commerce site can use an edge function to instantly show a localized promotion based on the user's region, without a slow round-trip to the main server.
Platforms like Vercel and Netlify have integrated edge functions directly into their frontend frameworks, making it seamless for developers to enhance Jamstack sites with powerful serverless logic. This makes it an invaluable tool for any application where performance directly impacts user engagement and conversion rates.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Start with Non-Critical Functions: Begin by offloading simple, low-risk logic to the edge, such as redirect handling or header manipulation. This allows your team to gain experience with the new paradigm before migrating mission-critical operations.
- Design for Quick Execution: Edge functions have strict execution time limits. Design your logic to be highly efficient and stateless to avoid timeouts and ensure rapid responses.
- Implement Comprehensive Monitoring: Use tools provided by your platform (e.g., Cloudflare Analytics, Vercel Logs) to monitor function performance, errors, and execution costs. Always set up alerting to catch issues before they impact users.
3. Headless & Composable CMS Architectures
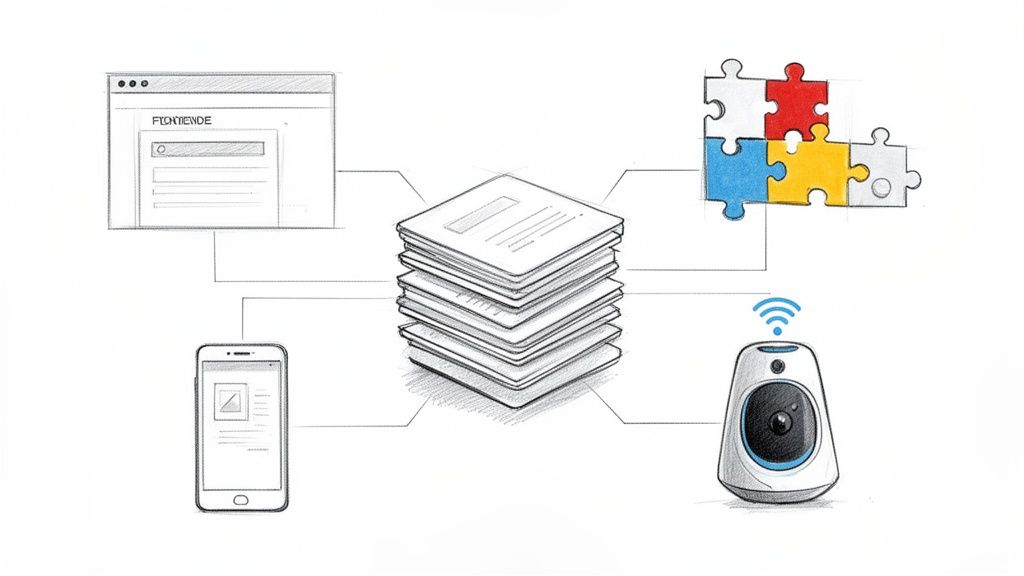
The move away from monolithic, all-in-one platforms marks a significant shift in how modern digital experiences are built. Headless and composable architectures are at the forefront of this web development trend, decoupling the content management backend (where content is created and stored) from the frontend presentation layer (what the user sees). This API-first approach allows content to be delivered to any channel, be it a website, mobile app, or IoT device, from a single source of truth.
Composable architecture takes this a step further, allowing teams to assemble a "best-of-breed" technology stack by integrating specialized services for functions like search, e-commerce, and personalization. This grants unparalleled flexibility, future-proofing your digital presence and avoiding vendor lock-in. For example, platforms like Contentful or Sanity.io are often combined with Next.js frontends to create incredibly fast and scalable user experiences.
When and Why to Use This Approach
This architecture is ideal for businesses managing content across multiple platforms or planning for future expansion into new digital channels. If you need to power a corporate website, a native mobile app, and in-store digital displays from one content repository, a headless CMS is the solution. It's also perfect for performance-focused projects, as decoupling allows for highly optimized frontends using modern frameworks like React or Vue.
Composable architectures shine when you require specialized functionality that a single platform cannot provide well. For instance, a brand could pair Shopify's headless e-commerce engine with Contentful for rich marketing content and Algolia for advanced search, creating a custom solution that excels in every area.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Prioritize the Developer Experience: When selecting a headless CMS, evaluate its APIs, documentation, and SDKs. A system that is difficult for your developers to work with will negate any potential productivity gains.
- Implement GraphQL for Efficient Queries: Use GraphQL APIs to allow frontend applications to request only the specific data they need. This reduces payload sizes and minimizes the number of API calls, boosting performance.
- Leverage Webhooks for Real-Time Updates: Configure webhooks in your CMS to trigger automated builds and cache invalidations whenever content is updated. This ensures your static sites or applications always display the latest information without manual intervention.
- Document API Contracts Thoroughly: Create clear and comprehensive documentation for your content models and API endpoints. This is crucial for enabling frontend and backend teams to work in parallel effectively.
4. Web Components & Micro Frontends
The shift toward modular, scalable, and independently maintainable applications has propelled Web Components and Micro Frontends to the forefront of web development trends. Web Components are a set of browser-native APIs that allow you to create reusable, encapsulated custom HTML elements. Micro Frontends take this concept to an architectural level, breaking down a large monolithic frontend into smaller, more manageable pieces that can be developed, tested, and deployed independently by different teams.
This approach empowers large organizations to scale their development efforts without creating bottlenecks. Teams can work autonomously on their specific feature or part of the application, using their preferred tech stack, and then seamlessly integrate their work into a cohesive user experience. Companies like Shopify and Zalando leverage this model to manage complexity and accelerate innovation across their vast digital platforms.
When and Why to Use This Approach
This architecture is ideal for large-scale enterprise applications where multiple teams contribute to a single user interface. Use it when you need to avoid the pitfalls of a monolithic frontend, such as slow build times, complex codebases, and deployment dependencies. For example, an e-commerce site can have separate micro frontends for product search, the shopping cart, and user reviews, each managed by a dedicated team.
This allows for technology-agnostic development, as one team can use React while another uses Vue, all integrated into the same shell. It significantly improves team autonomy and allows for incremental upgrades and easier maintenance, making it a powerful strategy for future-proofing complex digital products.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Establish Clear APIs: Define strict contracts and communication protocols between micro frontends. This ensures that changes in one part of the application do not unintentionally break another.
- Leverage Module Federation: Use tools like Webpack's Module Federation to share code and dependencies between different frontends efficiently, reducing redundant code and bundle size.
- Version Components Independently: Manage and version each micro frontend or component separately. This allows teams to deploy updates on their own schedule without coordinating a massive, high-risk "big bang" release. Always document integration points and breaking changes thoroughly.
5. Zero-Trust Security & Web Application Security
The traditional "castle-and-moat" security model, which trusts anyone inside the network perimeter, is officially obsolete. The modern web development landscape, with its distributed services, remote teams, and complex supply chains, demands a more rigorous approach. This is where a Zero-Trust architecture becomes a critical web development trend, fundamentally shifting the security paradigm to "never trust, always verify."
This model assumes that threats exist both outside and inside the network, so it requires strict identity verification and authorization for every person and device trying to access resources. This is coupled with a renewed focus on comprehensive Web Application Security, covering everything from API protection and content policies to automated vulnerability scanning. Tools like Okta, Cloudflare's Zero Trust platform, and Auth0 are making this once-complex architecture accessible to organizations of all sizes.
When and Why to Use This Approach
A Zero-Trust framework should be adopted in any environment with distributed architecture, remote or hybrid work models, or sensitive data. It is essential for protecting microservices, securing access to cloud infrastructure, and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations. For instance, instead of granting a developer broad access to a production database via a VPN, Zero-Trust grants them temporary, role-based access to only the specific tables they need for a specific task, after verifying their identity via multi-factor authentication (MFA).
This granular control minimizes the potential damage from a compromised account or device, making it an indispensable strategy for modern digital businesses. Adopting this model is a core tenet of the shift-left security movement, which integrates security practices earlier in the development lifecycle.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Implement MFA Everywhere: Enforce multi-factor authentication for all users and services, from developer tools to administrative dashboards. This is the foundational layer of any Zero-Trust strategy.
- Use API Gateways: Centralize API traffic through a gateway to enforce consistent security policies, authentication, and rate-limiting across all your microservices.
- Automate Security Scanning: Integrate tools like Snyk or OWASP ZAP into your CI/CD pipeline to automatically scan for vulnerabilities before code is deployed. Beyond this, developers must also implement these 10 essential website security best practices to protect applications from a wide range of threats.
- Monitor and Log All Access: Always maintain detailed logs of all access attempts and activities. Use this data to detect and respond to anomalous behavior in real-time.
6. TypeScript & Type-Safe Development
The move toward TypeScript and type-safe development represents a significant maturity in the JavaScript ecosystem. By adding a static type system on top of JavaScript, TypeScript allows developers to catch potential errors during the build process, long before the code ever reaches a user's browser. This web development trend is about writing more robust, predictable, and self-documenting code that scales effectively for complex applications.
This proactive approach to error prevention minimizes runtime bugs, simplifies refactoring, and dramatically improves the developer experience with features like intelligent autocompletion. The trend extends beyond the frontend, with tools like tRPC enabling end-to-end type safety from the database to the UI, ensuring data consistency across the entire stack. Major companies like Slack, Figma, and Stripe leverage TypeScript to maintain their large-scale applications.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Adopting TypeScript is ideal for large-scale, long-term projects with multiple developers. The bigger the codebase and the team, the more valuable static typing becomes for maintaining code quality and preventing regressions. Use it when building complex user interfaces, designing reusable component libraries, or creating APIs where the data contract between the client and server is critical.
For example, when using a data-fetching library like React Query with TypeScript, you can ensure that the data you receive from an API perfectly matches the shape your components expect. This eliminates a whole class of common bugs related to mismatched or unexpected data structures, making the application far more reliable.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Start with a Strict Configuration: When beginning a new project, enable
strictmode in yourtsconfig.jsonfile. This enforces best practices and maximizes TypeScript's error-checking capabilities from day one. - Gradually Migrate Existing Projects: You don't need to convert an entire JavaScript project at once. Rename files from
.jsto.tsone by one and incrementally add types, allowing for a phased and manageable adoption. - Implement End-to-End Typing: Explore tools like tRPC or code-generation with GraphQL to create a single source of truth for your data types. This ensures your frontend and backend are always in sync, preventing API integration errors.
- Leverage Type Inference: Let TypeScript infer types whenever possible. Instead of explicitly typing every variable, rely on inference to keep your code clean and reduce boilerplate while still benefiting from type safety.
7. AI-Driven UX/UI Design & Personalization
Beyond just assisting with code, Artificial Intelligence is revolutionizing the creative and user-centric aspects of web development. This trend leverages AI to automate and enhance the design process while delivering deeply personalized user experiences on the front end. Tools like Adobe Firefly generate design assets from text prompts, and Figma plugins automate repetitive design tasks, freeing up designers to focus on high-level user experience strategy.
On the product side, AI powers sophisticated personalization engines. Instead of a one-size-fits-all interface, AI analyzes user behavior, historical data, and context in real-time to tailor content, recommendations, and even the layout. This is exemplified by Netflix's content recommendation algorithm and Amazon's product suggestions, which create unique, engaging experiences that drive conversions and user retention.
When and Why to Use This Approach
This approach is invaluable for e-commerce platforms, content-heavy websites, and subscription services where user engagement is a key metric. Use it to increase conversion rates by showing users the most relevant products or to boost time-on-site by suggesting articles and videos tailored to their interests. For example, a travel website can use AI to dynamically adjust its homepage to feature beach destinations for a user who previously searched for tropical vacations.
By creating these adaptive and highly relevant interfaces, you move from a static web page to a dynamic, personal conversation with each user. This shift toward a more futuristic user interface design is a critical component of modern web development trends, setting market leaders apart from the competition by making users feel uniquely understood and valued.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Collect Data Ethically: Always obtain explicit user consent before collecting data for personalization. Be transparent about what data you collect and how it is used to build trust.
- Balance Personalization and Privacy: Implement robust data privacy controls and allow users to manage their personalization settings. Avoid creating filter bubbles by occasionally introducing diverse or popular content.
- Test for Bias: Regularly audit your personalization algorithms to ensure they are not creating unfair or biased outcomes for different user segments. Use A/B testing tools like Optimizely to validate the impact of your AI-driven experiments.
- Implement Fallback Experiences: Design a default, non-personalized experience for new users or those who have opted out of data collection. This ensures a solid baseline experience for everyone.
8. Progressive Web Apps (PWA) & Web Performance Optimization
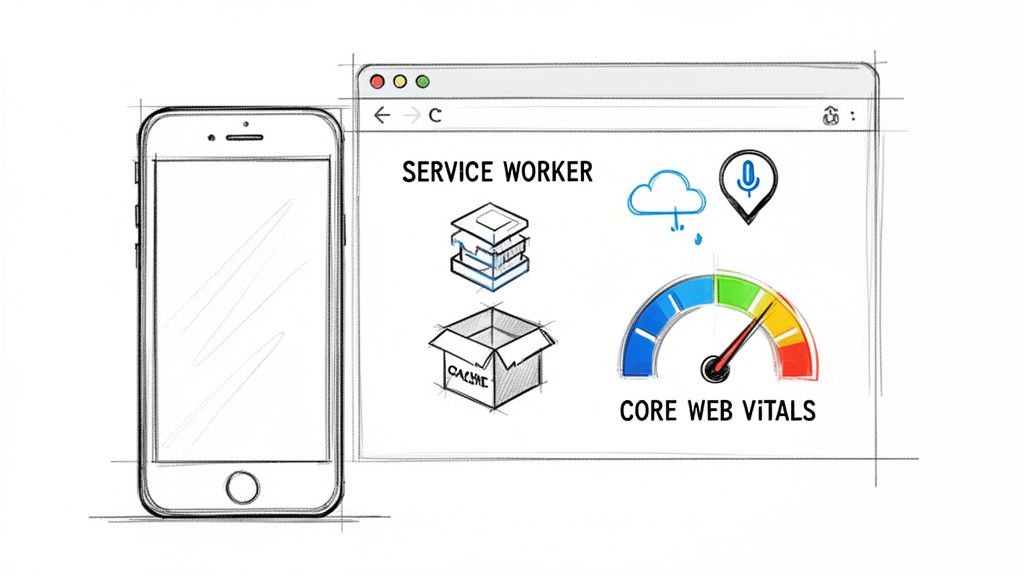
Progressive Web Apps (PWA) represent a pivotal evolution in web technology, blurring the lines between websites and native mobile applications. This web development trend leverages modern browser capabilities to deliver reliable, fast, and engaging user experiences. PWAs use service workers for offline functionality and background processing, a web app manifest to be "installable" on a user's home screen, and push notifications to re-engage users, all without the friction of an app store.
This is tightly coupled with a relentless focus on web performance optimization, particularly Google's Core Web Vitals (CWV). By optimizing for metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), developers ensure that these app-like experiences are also incredibly fast and responsive. The result is a user experience that rivals native apps while retaining the web's inherent reach and accessibility.
When and Why to Use This Approach
Adopting a PWA strategy is ideal for businesses aiming to increase user engagement, improve conversion rates, and provide a consistent experience across all devices. It is particularly powerful for e-commerce sites, news publishers, and social media platforms where repeat visits and offline access are critical. For example, the Starbucks PWA allows customers to browse the menu and customize their orders offline, submitting them once they reconnect. This convenience directly translates to improved customer loyalty and sales.
This trend is also crucial for companies targeting markets with inconsistent internet connectivity. By caching key assets, a PWA remains functional even in poor network conditions, a significant advantage over a traditional website. Case studies like the Twitter Lite PWA, which saw a 75% increase in Tweets sent, prove its effectiveness at scale.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Audit with Lighthouse: Regularly use Google's Lighthouse tool to audit your PWA capabilities and performance. It provides a clear checklist for PWA compliance and detailed recommendations for improving your Core Web Vitals score.
- Implement a Caching Strategy: Use service workers to define a robust caching strategy. Start with caching the application shell (HTML, CSS, JS) and gradually add caching for dynamic content or API responses to enable meaningful offline functionality.
- Optimize for Core Web Vitals: Aggressively optimize images using modern formats like WebP or AVIF, defer non-critical CSS and JavaScript, and pre-load key resources to drastically improve your LCP and FID scores. Dive deeper into these techniques to learn how to improve website speed for a better user experience and SEO ranking.
- Secure Your Site with HTTPS: A PWA must be served over HTTPS. This is a non-negotiable security prerequisite for enabling service workers and other key PWA features.
9. GraphQL & API-First Development
The move towards a decoupled, API-first architecture represents a mature evolution in web development trends, with GraphQL at its forefront. This approach prioritizes designing robust APIs before any frontend or backend implementation begins. GraphQL, a query language for your API, empowers clients to request exactly the data they need and nothing more, solving the chronic issues of over-fetching and under-fetching common with traditional REST APIs. This precision leads to faster, more efficient applications.
This paradigm shift ensures that frontend and backend teams can work in parallel, guided by a clear and stable API contract. For organizations like GitHub and Shopify, which offer complex data access to third-party developers, GraphQL provides the flexibility and power needed to build sophisticated integrations without constant backend changes. It creates a self-documenting, strongly-typed gateway to your data services.
When and Why to Use This Approach
An API-first strategy with GraphQL is ideal for applications with complex data requirements, multiple client platforms (web, mobile, IoT), or a microservices architecture. Use it when your frontend needs to fetch data from several different sources to build a single view. For example, an e-commerce product page might need product details, inventory status, and user reviews from three separate microservices. With GraphQL, the client can make a single, precise query to an API gateway to retrieve all that data at once.
This approach is invaluable for teams aiming to scale development and improve collaboration. By defining the API contract first using tools like Apollo Studio, you establish a single source of truth that decouples development cycles, allowing teams to build and test independently and accelerating time-to-market.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Solve N+1 Problems: Use a batching and caching solution like the DataLoader pattern to prevent the classic N+1 query problem, where fetching a list of items results in an excessive number of database calls.
- Secure Your Endpoint: Implement security measures like query depth and complexity limits to protect your API from malicious or poorly formed queries that could overload your servers.
- Embrace Strong Tooling: Leverage a comprehensive client like Apollo Client or Relay to handle caching, state management, and real-time data synchronization on the frontend, which drastically simplifies development.
- Monitor Performance: Always monitor the performance of your GraphQL queries. Identify slow resolvers and hot paths to optimize your data-fetching logic and ensure a responsive user experience.
10. Low-Code/No-Code Platforms & Composable Development
The rise of low-code/no-code (LCNC) platforms marks a significant shift in who can build and deploy applications, democratizing the development process. This web development trend empowers non-technical users and business teams to create functional software using visual interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and configuration instead of traditional coding. Composable development complements this by allowing teams to assemble applications from pre-built, API-first services and components rather than building every feature from scratch.
This approach dramatically accelerates development cycles, enabling rapid prototyping and the launch of Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) in a fraction of the time. Platforms like Bubble and Webflow allow for the creation of sophisticated, data-driven web applications and visually stunning websites without writing a single line of code, empowering entrepreneurs and marketing teams to bring their ideas to life independently.
When and Why to Use This Approach
LCNC is ideal for building internal tools, standard business applications, automating workflows, and validating market ideas quickly. Use it for creating customer relationship management (CRM) systems, project management dashboards, or applications that rely on standard CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. For example, a marketing team could use a tool like Airtable to build a content management database and use Zapier to automate its distribution across social media channels, all without developer intervention.
This strategy is particularly powerful for startups seeking to test a business concept with minimal initial investment. Building an MVP on a platform like Bubble allows for quick market validation and user feedback collection before committing to the significant resources required for a full-code custom build.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Validate Ideas with an MVP: Leverage LCNC platforms to build and launch an MVP quickly. This is the fastest way to gather real-world user data and determine if there is a market for your product before scaling.
- Combine with Custom Code: Don't view it as an all-or-nothing choice. Many platforms allow you to inject custom HTML, CSS, or JavaScript, or connect to custom APIs, giving you the flexibility to handle complex requirements that go beyond the platform's native capabilities.
- Prioritize Data Portability: Before committing to a platform, ensure it offers robust data export capabilities. This is critical for maintaining flexibility and ensuring you can migrate to a full-code solution in the future as your application scales and its needs evolve.
Top 10 Web Development Trends Comparison
| Trend / Technology | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages ⭐ | Tips 💡 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Development & Code Generation | Moderate — integrate IDEs/CI with validation workflows | External AI services, compute, developer oversight | Faster development, improved consistency, lower TTM | Boilerplate, testing, onboarding, staff augmentation | Accelerates dev; reduces repetitive work; improves quality | Enforce code review; train prompts; use for routine code |
| Edge Computing & Serverless Architectures | Medium–High — design distributed functions and observability | Cloud edge nodes, CDNs, provider-managed services | Ultra-low latency, automatic scaling, pay-per-use cost model | Real-time APIs, IoT, globally distributed apps | Low ops overhead; scalable; faster responses | Start with non-critical funcs; monitor; optimize cold starts |
| Headless & Composable CMS Architectures | High — API-first integration and orchestration | Multiple SaaS products, CDNs, API engineering | Flexible multi-channel delivery; faster content updates | Content-rich sites, omnichannel, marketing-driven projects | Frontend freedom; content reuse; independent scaling | Use GraphQL/webhooks; cache at edge; document APIs |
| Web Components & Micro Frontends | High — state, integration, and versioning complexity | Team coordination, module federation tooling, CI/CD | Parallel dev, reusable UI, smaller bundles via code-splitting | Large orgs, multi-team frontends, UI libraries | Independent deployments; framework-agnostic reuse | Define clear contracts; use module federation; version deliberately |
| Zero-Trust Security & Web App Security | High — architectural changes and continuous verification | IAM, monitoring, scanning tools, ongoing ops | Reduced breach impact, better compliance, faster detection | Enterprises, sensitive-data apps, remote-work environments | Stronger security posture; compliance leadership | Enforce MFA; automate scans in CI/CD; log and monitor all access |
| TypeScript & Type-Safe Development | Low–Medium — tooling and gradual migration effort | Developer time to learn, build step adjustments | Fewer runtime bugs, easier refactors, improved DX | Large codebases, API-centric apps, cross-team projects | Early bug detection; stronger maintainability | Adopt strict tsconfig; migrate gradually; use community types |
| AI-Driven UX/UI Design & Personalization | Medium–High — data pipelines and model integration | User data, analytics, ML models, experimentation tools | Higher engagement and conversion via tailored experiences | E‑commerce, media, SaaS with personalization needs | Scalable personalization; faster design iteration | Collect consent; test for bias; provide fallback experiences |
| Progressive Web Apps & Web Performance Optimization | Medium — service workers, caching, and tuning | CDNs, monitoring tools, performance auditing (Lighthouse) | Offline support, improved Core Web Vitals, higher retention | Markets with poor connectivity, content apps, startups | App-like UX without app stores; better SEO | Prioritize Core Web Vitals; implement caching strategies; audit continuously |
| GraphQL & API-First Development | Medium–High — schema design and resolver optimization | Backend engineering, GraphQL tooling, monitoring | Precise data delivery, improved frontend/backend decoupling | Complex data models, many client types, mobile apps | Eliminates over/under-fetching; self-documenting APIs | Use DataLoader; limit query depth; monitor query performance |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms & Composable Development | Low for MVPs, higher for complex integrations | Platform subscriptions, business-user training, limited dev time | Rapid prototyping, lower initial dev cost, faster validation | MVPs, internal tools, non-critical customer workflows | Fast time-to-market; empowers non-dev stakeholders | Ensure data export; combine with custom code for complexity |
Turning Trends into Triumph: Your Next Steps with Nerdify
The digital landscape is in a state of perpetual motion, and the web development trends we've explored are not just fleeting fads; they are the fundamental building blocks of tomorrow's user experiences. From the intelligent automation of AI-powered code generation and the hyper-personalization of AI-driven UX to the resilient, scalable foundations laid by edge computing and headless architectures, a clear pattern emerges. The future of the web is smarter, faster, more secure, and infinitely more composable.
Navigating this complex terrain can feel daunting. The sheer number of innovations, from the type-safe reliability of TypeScript to the granular control of GraphQL, requires a strategic, forward-thinking approach. Simply knowing about these trends is not enough. The real challenge, and the greatest opportunity, lies in integrating them effectively to create tangible business value. This means moving beyond theory and into strategic implementation.
From Information to Action: A Strategic Roadmap
The journey from understanding web development trends to leveraging them for competitive advantage requires a clear plan. It's about making deliberate choices that align with your specific business goals, technical capabilities, and user expectations. Waiting for these trends to become mainstream is a strategy for falling behind; proactive adoption is the key to leadership.
Here are the actionable next steps to translate these insights into a powerful digital strategy:
- Conduct a Technology Audit: Begin by evaluating your current technology stack. Where are the bottlenecks? Identify which of the trends discussed, such as migrating to a headless CMS or adopting GraphQL, could directly solve your most pressing performance, scalability, or content management challenges.
- Prioritize Based on Impact: You don't need to adopt every trend at once. Rank them based on potential ROI for your business. For an e-commerce platform, PWA implementation might offer the biggest immediate lift in mobile conversions. For a data-heavy SaaS application, adopting TypeScript could be a top priority to reduce bugs and improve long-term maintainability.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Choose a small, low-risk project to experiment with a new technology. For example, build a single micro frontend using web components or develop a new internal tool on a low-code platform. This allows your team to learn, adapt, and demonstrate value without disrupting core business operations.
- Upskill and Augment Your Team: The demand for expertise in areas like WebAssembly, serverless functions, and AI integration is high. Invest in training for your existing team or bridge the gap with expert staff augmentation. Bringing in specialists like Nerdify’s developers can accelerate your adoption curve and ensure you implement these technologies according to best practices from day one.
Partnering for a Future-Proof Digital Presence
The overarching theme connecting these web development trends is a move toward more modular, intelligent, and user-centric systems. This is not just a technological shift; it's a strategic one. It's about building digital platforms that are not monolithic and rigid, but adaptable and resilient, ready to evolve with your business and your customers' needs.
At Nerdify, we live at the intersection of these trends. Our expertise isn't just in writing code; it's in architecting solutions that harness the power of these innovations. Whether it's designing a composable architecture that gives your marketing team unparalleled agility or implementing a zero-trust security model to protect your most valuable assets, we are your strategic partner in building for what's next.
The future of web development is already here. It’s an ecosystem of powerful, interconnected technologies waiting to be harnessed. By taking these deliberate, strategic steps, you can move from being a spectator of change to a leader who shapes it, creating digital experiences that are not only current but truly triumphant.