A Guide to Custom Software Development Services

When you hear the term custom software development services, think of it less as a product and more as a process. It’s the journey of designing, building, and maintaining software that’s made specifically for your business—your team, your customers, and your unique challenges.
The easiest way to grasp this is the classic tailored suit analogy. An off-the-rack suit might look fine, but it was made for the average person. A tailored suit, however, is cut and stitched to fit you perfectly, enhancing your best features and moving with you. Custom software does the same for your business operations.
Why Go Custom When Off-the-Shelf Exists?
Ready-made software is designed for the masses. This means it often comes loaded with features you'll never touch, while somehow missing the one or two critical functions you desperately need. This forces you to change your proven workflows to fit the software's rigid structure.
In stark contrast, custom software is built to wrap around your existing processes. It digitizes and enhances what you already do best, making your team more efficient from the moment they log in. This isn't just about making things easier; it's a powerful strategic move. Companies that invest in custom solutions can pivot faster, create truly unique customer experiences, and build a competitive edge that generic software can't match.
The Real-World Advantages of a Custom Build
Building your own application delivers concrete benefits that show up on your balance sheet and in your daily operations. While there's an upfront investment, it often pays for itself by eliminating endless subscription fees and ensuring you're only paying for functionality you actually use.
Here’s what you really gain:
- Rock-Solid Security: You're in complete control of the security measures. This makes it far simpler to safeguard sensitive information and meet strict compliance standards like HIPAA or ISO.
- Built-in Scalability: Your software should grow with your business, not hold it back. A custom solution is engineered from the ground up to handle more users, more data, and more complexity as you expand.
- Flawless Integration: Ever tried to get two off-the-shelf tools to talk to each other? It can be a nightmare. A custom app is designed to connect seamlessly with your other essential systems, like your CRM or ERP, creating a single, unified data pipeline.
The core mission of custom software is to take your specific operational headaches and turn them into a smooth, efficient, and scalable digital tool. It makes technology bend to your business needs, not the other way around.
Ultimately, choosing custom development is about taking back control. You own the code and the intellectual property, which gives you total freedom over the software’s future. For a closer look at how different development models can provide this control, a guide to nearshore software development services offers some great insights.
And if you're curious about the different types of tailored software out there, our overview of custom software development solutions is a great place to start. This ownership is what ensures your software remains a valuable, relevant asset for the long haul.
The Custom Software Development Lifecycle
So, how does a simple idea turn into a real, working piece of software that can run a business? It all happens through a structured journey called the custom software development lifecycle. This isn't just a technical checklist; it's a creative and collaborative process.
Think of it like building a custom home. Each phase builds on the last, making sure the final structure is solid, functional, and exactly what the owner envisioned.
This methodical approach is more important than ever. The global market for custom software has exploded, reaching USD 43.21 billion and is expected to climb to USD 53.02 billion next year. With that much at stake, a well-managed development process is the key to success. You can dig deeper into these numbers in this custom software development market report.

To help visualize this journey, here’s a quick overview of the six key phases.
Overview of the Software Development Lifecycle
This table breaks down each stage of the development lifecycle, from the initial idea to post-launch support.
| Phase | Primary Goal | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery | To define project goals and create a detailed roadmap. | Stakeholder interviews, market analysis, feature mapping, technical feasibility studies. |
| UX/UI Design | To design an intuitive and visually appealing user interface. | Wireframing, prototyping, user journey mapping, visual design, branding. |
| Development | To write the code and build the functional software. | Backend (server, database) and frontend (user interface) coding, API integration. |
| Quality Assurance | To find and fix bugs, ensuring the software is stable and secure. | Functional testing, performance testing, security audits, user acceptance testing. |
| Deployment | To launch the application and make it available to users. | Server setup, data migration, go-live checklists, performance monitoring. |
| Maintenance | To provide ongoing support, updates, and improvements. | Bug fixes, security patches, feature enhancements, performance optimization. |
Each phase is a critical step in turning your vision into a reliable, high-performing application. Let's explore what happens in each one.
Stage 1: Discovery — The Architectural Blueprint
Every great project starts with a conversation, not a line of code. The Discovery phase is where your development partner acts like an architect, sitting down with you to sketch out a detailed blueprint. This first stage is all about understanding the "why" behind your project.
During discovery, the team dives deep into your business. They’ll define the core objectives, figure out who your target users are, and map out the must-have features. It’s a mix of stakeholder interviews, market research, and technical reality checks.
The end goal is a rock-solid project scope, a clear roadmap, and a shared definition of what success looks like. Skipping or rushing this stage is like building a house without a blueprint—a surefire way to end up with costly mistakes and a product that doesn't fit your needs.
Stage 2: UX/UI Design — The Interior and Exterior
Once the blueprint is set, it's time to bring the vision to life visually. This phase focuses on how the software will look and feel, and it's broken down into two crucial components: User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI).
- UX Design (The Floorplan): This is the science behind making the software feel natural and easy to navigate. UX designers build wireframes and prototypes to map out user journeys, ensuring every click and interaction makes sense. It’s all about the logical flow.
- UI Design (The Aesthetics): This is the art of making the software look great. UI designers pick the colors, fonts, and icons that create a beautiful interface and reflect your brand. It’s the visual personality of your application.
Together, great UX and UI create software that isn't just powerful but is genuinely enjoyable to use.
Stage 3: Development — The Construction
With the design approved, the developers get to work. This is the "construction" phase where the visual designs and feature lists are translated into actual, working code.
First, they build the "foundation" (backend), which includes the server, database, and all the application logic that powers everything behind the scenes.
At the same time, they build the "walls and windows" (frontend)—the part of the application that users see and interact with. This stage often follows agile methods, breaking the work into small, manageable cycles called "sprints." For a closer look at this process, check out our guide on agile software development best practices.
This iterative approach allows for continuous feedback and adjustments, ensuring the project stays on track and aligned with your vision. It’s like building one room at a time and getting your approval before moving to the next.
Stage 4: Quality Assurance — The Final Inspection
Before anyone "moves in," the entire structure needs a thorough inspection. The Quality Assurance (QA) phase is a methodical process of testing the software to hunt down and fix any bugs, glitches, or performance issues.
QA engineers are the inspectors, running a battery of tests to make sure everything works perfectly. This typically includes:
- Functional Testing: Checking that every feature does exactly what it's supposed to do.
- Performance Testing: Pushing the software to its limits to test speed, responsiveness, and stability.
- Security Testing: Probing for vulnerabilities to make sure user data is safe and secure.
This rigorous testing ensures the final product is stable, reliable, and ready for the real world.
Stage 5: Deployment — Moving In
Once the software has passed every inspection, it’s time for Deployment. This is the exciting moment your application goes live and becomes available to your users. The process involves setting up the live server environment, migrating any necessary data, and flipping the switch.
A good deployment team makes this transition feel seamless, with zero downtime or disruption for your business.
Stage 6: Maintenance — Ongoing Upkeep
A house needs maintenance to stay in great shape, and software is no different. The final phase, Maintenance, is all about providing support after the launch.
This crucial, ongoing stage involves monitoring performance, fixing any new bugs that pop up, and rolling out regular updates. This keeps your software secure, compatible with new operating systems and browsers, and ensures it continues to provide value long after day one.
Choosing Your Pricing and Engagement Model
Once the blueprint for your software is ready, it's time to talk money and how you'll work together. This isn't just about the final bill; it’s about picking a partnership structure that fits your project's goals, budget, and need for wiggle room. Getting this right from the start is fundamental to a successful project, ensuring everyone is on the same page.
Think of it like hiring any expert. You could hire a caterer for a fixed fee to deliver a specific menu for an event. Or, you might hire a consultant by the hour for their evolving advice. Each approach has its place, and understanding the differences is key to making a smart investment in custom software development services.
The Fixed Price Model For Predictable Projects
The Fixed Price model is as straightforward as it gets: one price for one specific scope of work. It’s the perfect choice when your project requirements are locked down, thoroughly documented, and you’re confident they won’t change. This model gives you total budget predictability, a huge win for any business keeping a close eye on the bottom line.
It’s like ordering that wedding catering. You agree on the menu, guest count, and final price months ahead of time. The caterer is on the hook to deliver exactly what was promised, for that exact cost. Simple.
But the very thing that makes this model strong—its rigidity—is also its biggest weakness. If you realize halfway through that you need a new feature, it means hitting the brakes and drafting a formal change request. That almost always leads to extra costs and a longer timeline.
- Best for: Projects with a rock-solid, clearly defined scope, like building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) or a simple internal tool.
- Pros: You know exactly what you'll pay, which minimizes financial risk.
- Cons: There’s very little flexibility, and scope changes can become a real headache.
The Time and Materials Model For Agile Projects
On the other end of the spectrum, the Time & Materials (T&M) model is all about flexibility. You pay for the actual hours the development team puts in, plus the cost of any tools or third-party services they need. This is the go-to approach for complex, long-term projects where you know the scope will probably shift and evolve.
Think of this as hiring a great contractor to renovate your house. You pay for their time and the materials they buy. If you decide on a whim to add a skylight or move a wall, they can roll with it because the agreement is based on effort, not a pre-defined outcome.
This model is a natural fit for agile development, where the project is built in short, iterative cycles. It allows for constant feedback and tweaks, ensuring the final product is something the market actually wants. The secret to making T&M work is tight communication and transparent time-tracking to keep the budget on track. If you want a deeper dive, you can learn more about how different software development pricing models stack up.
The Time & Materials model trades the budget certainty of a fixed price for the invaluable ability to adapt and innovate as the project progresses.
The Nearshore Staff Augmentation Model For Team Integration
Sometimes, you don't need a development partner to build an entire project from the ground up. You just have a skills gap on your own team that needs filling. That's where Nearshore Staff Augmentation shines. In this model, you essentially "rent" developers from a partner agency who then become a fully integrated part of your in-house team.
It’s like adding a specialized wing to your existing office. You're not handing the project off; you're bringing in experts who work side-by-side with your people, report to your managers, and follow your company’s way of doing things. The "nearshore" part is a huge bonus—it means the developers are in a similar time zone, which cuts out the frustrating communication lag you often get with offshore teams. You get the talent you need without the cost and commitment of hiring new full-time employees.
What You Actually Get: A Look at Your Tech Stack and Project Deliverables
When you hire a team for custom software development, what do you actually end up with? It’s more than just a functioning app. You get a set of concrete deliverables built on a specific technology stack—together, they’re the digital DNA of your project. Getting a handle on these terms isn’t just for techies; it helps you have smarter conversations with your development team and truly understand what you're paying for.
Let's start with the tech stack. Think of it like a chef's kitchen. To cook a gourmet meal (your software), you need the right set of tools—the ovens, stoves, knives, and ingredients. In the software world, these tools are the programming languages, frameworks, databases, and servers that developers use to bring your application to life.
Choosing a tech stack isn't about picking the trendiest new technology. It’s a strategic decision that directly affects your software's performance, security, and ability to grow with your business. The right stack makes all the difference.
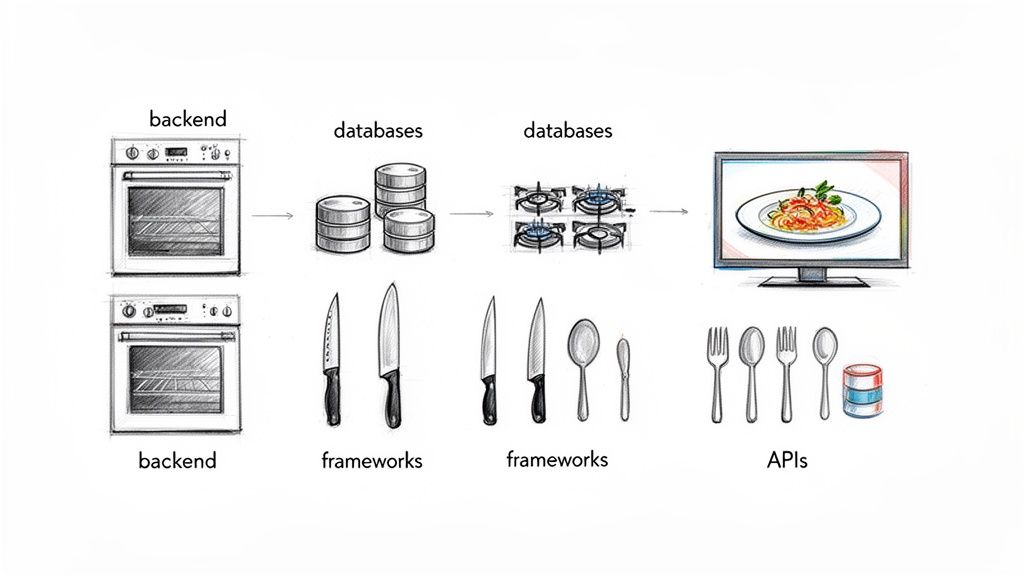
Breaking Down the Tech Stack
While the exact combination of tools will vary, most technology stacks are built with a few core layers. Each layer has a specific job, and they all work together to create a seamless experience.
The Frontend (What Your Users See): This is everything a user can see and interact with on their screen—the buttons they click, the menus they navigate, and the overall layout. It’s the visual part of the application, typically built with frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js.
The Backend (The Engine Room): If the frontend is the car's dashboard, the backend is the engine. It's the server-side logic that does all the heavy lifting: processing data, managing user accounts, and talking to the database. Popular backend technologies include Node.js, Python, PHP, and Java.
The Database (Your Digital Filing Cabinet): This is where all the application's information is stored, organized, and retrieved. Whether it’s user profiles, product inventory, or blog posts, the database keeps it safe and accessible. Common choices include relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL, or NoSQL databases like MongoDB.
Server & Hosting (The Foundation): Your application needs a place to live. The server and hosting infrastructure provide the physical or virtual space where your software runs. Today, most projects rely on cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Cloud for their reliability and scalability.
The best tech stack is the one that fits your business goals like a glove. It’s not about flashy trends, but about choosing the right, sturdy tools to build a product that’s reliable, scalable, and easy to maintain down the road.
What Ends Up in Your Hands: Common Project Deliverables
So, the tech stack is the "how," but what about the "what"? Your project will produce tangible assets called deliverables. These are the actual products you receive at the end of the process.
Let’s unpack the most common ones.
Web Applications
A web application is a program that runs in your browser. Unlike a static website that just shows information, a web app is fully interactive. Think of complex tools like Google Docs, the Salesforce CRM, or your online banking portal—these are all web apps.
Their biggest advantage is accessibility. Anyone with a browser can use them, which means you can reach a massive audience without forcing anyone to download or install a thing. They are the workhorses of the modern business world.
Mobile Applications
Mobile apps are built from the ground up for smartphones and tablets. They deliver a slick, optimized experience and can often work offline. You’ll typically encounter two main flavors:
Native Apps: These are built specifically for one operating system—either iOS or Android. Because they are "native" to the device, they offer the best performance and can tap directly into features like the camera, GPS, and push notifications.
Cross-Platform Apps: These are built with a single codebase that runs on both iOS and Android, using frameworks like React Native or Flutter. This approach can be more cost-effective and get your app to market much faster.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
Think of an API as a waiter in a restaurant. It takes your order (a request for data) to the kitchen (the backend server) and brings back your food (the data you need). APIs allow different software systems to talk to each other securely and efficiently.
For example, a travel aggregator site uses APIs to pull real-time flight information from dozens of different airlines into one place. A custom-built API is a huge asset. It can create new revenue streams by letting partners plug into your system, or it can be the central hub that powers all your own web and mobile apps. It’s the key to building a connected, scalable digital ecosystem.
How to Choose the Right Software Development Partner
Picking a partner for your custom software project is probably the single most important decision you'll make. Get it right, and the agency becomes a seamless extension of your team—a true partner invested in your success. Get it wrong, and you’re looking at blown budgets, missed deadlines, and a final product that just doesn't hit the mark.
This isn't about hiring a group of coders. It's about finding a team that genuinely gets your business, communicates like a pro, and has a battle-tested process for handling the twists and turns that always pop up in a big project. A great partnership really boils down to three things: competence, chemistry, and trust.
To make the right call, you need a solid plan to vet potential agencies, looking past the fancy slide decks to see how they actually operate.
Portfolios and Case Studies Tell the Real Story
A portfolio should be more than a pretty gallery of screenshots. Think of it as a collection of success stories that show off a company's problem-solving chops. When you're looking through a potential partner's work, don't just skim the surface.
Try to find projects that feel similar to yours, whether in your industry, the scope of work, or the tech involved. That’s a good sign they won't be learning on your dime. Really dig into their case studies. How did they handle specific challenges? What concrete business results did they deliver for their clients?
A weak case study says, "We built an app." A strong one says, "We built an inventory management app that cut picking errors by 30% and saved the client $50,000 in its first year." You want to see real numbers and tangible outcomes.
The Make-or-Break Questions to Ask
Once you have a shortlist, it's time to start talking. The questions you ask are your best tool for uncovering how they work, how they communicate, and what happens when things don't go according to plan. This is your chance to see if their style really meshes with yours.
Here are a few essential questions to get the conversation started:
- What happens when we hit a roadblock or need to change the scope? Their answer here is telling. A great partner won't panic; they'll have a clear process for managing changes without throwing the whole project off the rails.
- Can we talk to a couple of your current clients? Past client testimonials are one thing, but talking to someone they're working with right now gives you an unfiltered look at their day-to-day communication and project management.
- What’s the technical background of your team? Get specific. Ask about their experience with the technologies your project needs, especially when it comes to the cloud. With cloud deployment making up a massive 67% of the market, you need to know your partner is fluent. You can find more details on this growing market at gminsights.com.
- Who will be our day-to-day contact? You need one clear point person. Knowing who that is from the get-go prevents a lot of headaches and crossed wires down the line.
To help organize your thoughts as you talk to different firms, a checklist can be incredibly useful.
Vendor Selection Checklist
Here’s a simple framework to help you evaluate and compare potential partners. Use it to keep your notes consistent and make a more objective decision when the time comes.
| Evaluation Area | What to Look For | Key Questions to Ask |
|---|---|---|
| Relevant Experience | Projects in your industry or with similar technical challenges. Evidence of solving problems like yours. | "Can you show me a project that had similar goals to ours?" "What was the biggest challenge on that project and how did you solve it?" |
| Technical Competence | Deep expertise in your required technology stack (e.g., specific languages, frameworks, cloud platforms). | "What is your team's experience with [Your Tech Stack]?" "How do you stay current with new technologies and best practices?" |
| Process & Methodology | A clear, well-defined development process (e.g., Agile, Scrum). A structured approach to project management. | "Can you walk me through your typical project lifecycle?" "How do you handle scope changes and feature requests mid-project?" |
| Communication & Culture | Proactive, clear, and frequent communication. A collaborative and problem-solving attitude. | "Who would be my main point of contact?" "What tools do you use for project communication and progress tracking?" |
| References & Reputation | Positive feedback from current and past clients. Strong online reviews and industry standing. | "May I speak with 1-2 of your current clients?" "What do your clients typically praise you for?" |
This checklist isn't about finding a vendor that scores a perfect 10/10. It’s about finding the one that best aligns with your specific needs, your team's culture, and your project's goals.
Don't Ignore These Red Flags
Knowing what to look for is only half the battle; you also need to know what to run from. Some warning signs early on can save you from a partnership that’s doomed from the start.
- Vague Proposals: If their proposal is fuzzy on deliverables, timelines, or costs, that’s a huge red flag. A professional firm will give you a detailed, transparent plan that leaves no room for "surprises."
- A Lack of Transparency: A partner who’s cagey about their process, won't let you talk to the team, or gets defensive when you ask for client references might be hiding something. Trust is everything.
- The "Yes" Person: It’s tempting to hire the team that says "yes" to everything. But a truly experienced partner knows when to push back. They’ll tell you when an idea might hurt the budget or timeline, and they’ll suggest better alternatives.
- Bad Communication from the Start: Pay close attention to how they communicate before you even sign a contract. If they're slow to respond, hard to understand, or just don't seem to be listening, that’s not going to get better once they have your business.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers.
When you're thinking about building custom software, a lot of practical questions pop up. How long will this take? What's the budget look like? Who actually owns the code when it's done? Getting clear answers to these things is the first step toward a successful project and a solid relationship with your development partner.
Let's tackle some of the most common questions we hear from businesses just like yours.
How Long Does It Take to Build Custom Software?
That's the million-dollar question, and the honest answer is always, "It depends." Think of it like building a house. A small, simple cottage will be ready much faster than a sprawling mansion with a custom pool and home theater.
The timeline for any custom software development services project really boils down to three things: its complexity, the number of features you need, and the size of the team working on it.
A lean Minimum Viable Product (MVP) with just the core, must-have features can often be up and running in 3-6 months. This is a great way to test an idea without a massive upfront commitment. On the other hand, a complex enterprise system that needs to integrate with a dozen other tools and has Fort Knox-level security could easily take a year or more.
The only way to get a truly reliable timeline is to go through a proper discovery phase. This is like creating the architectural blueprints before you start pouring concrete—it maps out every detail so there are no surprises down the road.
How Much Do Custom Software Services Cost?
Just like the timeline, the cost isn't a one-size-fits-all number. The final price tag is shaped by the project's scope, the technology we use to build it, and the type of engagement model you choose (like Fixed Price vs. Time & Materials).
It’s easy to get sticker shock, but it’s important to frame the cost as an investment in a long-term business asset, not just another line-item expense. The real payoff comes from the return on that investment.
A custom solution pays for itself over time by making your team more efficient, giving you a real edge over the competition, and creating a platform you can build on for years. You’re not just buying a piece of software; you’re investing in your company's future.
Who Owns the Intellectual Property and Source Code?
This one is a deal-breaker, and the answer should be crystal clear. When the project is done and paid for, you, the client, should own 100% of the intellectual property (IP) and the source code. Period.
Make sure this is spelled out explicitly in your contract. Any professional, trustworthy development firm will have this as a standard clause in every single agreement.
- Your Ownership: Having full ownership means you can do whatever you want with the software—modify it, scale it, or even sell it one day. No strings attached.
- No Vendor Lock-in: When you own the code, you're never stuck with one agency. If you decide to work with someone else for future updates, you can simply hand them the source code.
- A Massive Red Flag: If a potential partner gets vague or tries to retain ownership of the IP, walk away. That’s a sign of a bad partnership waiting to happen.
What Kind of Support Is Available After Launch?
Pushing the "go-live" button is just the beginning. Your software is now out in the real world, and it needs ongoing care to stay healthy and effective. That's where post-launch support and maintenance come in.
Most development partners offer support plans that cover the essentials:
- Bug Fixes: Squashing any little issues that pop up once real users start interacting with the software.
- Security Updates: Keeping your application protected from new and emerging threats.
- Performance Monitoring: Watching over the system's speed and stability to ensure everything runs smoothly.
- Feature Enhancements: Adding small improvements and new features based on feedback from your users.
A good partner will help you figure out a support plan that fits your needs and budget. The goal is to make sure your software continues to be a reliable and valuable tool for a long, long time. If you want to dig deeper, you can always explore more Frequently Asked Questions on the topic.